TX4939XBG-400 Toshiba, TX4939XBG-400 Datasheet - Page 458

TX4939XBG-400
Manufacturer Part Number
TX4939XBG-400
Description
Manufacturer
Toshiba
Datasheet
1.TX4939XBG-400.pdf
(740 pages)
Specifications of TX4939XBG-400
Cpu Core
TX49/H4 90nm
Clock Mhz/max Mips
400/520
Inst./data Cache
32KB (4 Way)/32KB (4 Way)
Tlb
x
1cycle Mac
x
Volts (v)
1.25/2.5/3.3
Peripherals
DDR, NAND, ATA, ETHERNET, SECURITY, FPU, MMU, SPI, I2S, I2C, PCI, VIDEO, UART, TIMER, RTC
Companion Chip
TC86C001FG
Package
PGBA456
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
TX4939XBG-400
Manufacturer:
NSC
Quantity:
872
Company:
Part Number:
TX4939XBG-400
Manufacturer:
TOSHIBA
Quantity:
10 440
Part Number:
TX4939XBG-400
Manufacturer:
TOSHIBA/东芝
Quantity:
20 000
- Current page: 458 of 740
- Download datasheet (7Mb)
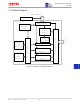
ATA100
Rev. 3.1 November 1, 2005
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Note :
Data register in ATA shadow register is 16 bits; all others are 8 bits. All ATA shadow registers are accessed on
Gbus byte boundaries. The Data register should be accessed with a word address of 0 and the two least
significant byte enables asserted. This will read or write the full 16-bit data register. If only the least significant
byte enable is asserted, the high-order byte of the data to or from the data register will be set to zero. If the
Gbus word address is 0 and byte enable 1 is the least significant one asserted, this is an access of the
Error/Feature register.
The ATA Controller does not support a 64-bit read/write to registers. So the read/write to DMA Command,
Status and PRD Table Pointer can not be combined. Use 32-bit load/store to read/write to PRD Table Pointer.
Every time user does a write to the Device/Head register, user must do a write to the System Control Register
for next command/data transfer immediately after the write to the Device/Head register.
A write to the Command register in the slave mapping module will cause to write the new value of the Direction
bit in the ATA100 Core and to write the new value of the Start bit in the ATA100 Core. Since the Status and
Command registers are within the same 32-bit word, it is possible to clear the status bits and write the R/W and
Start bit in the same Gbus write operation. But please take consideration on access order. The status bits will
be cleared first, then the R/W bit will be written to the correct value and finally the start bit will be written. When
both the R_OR_WCTR bit (direction bit) and START_STOPBM bit (start bit) are written in the same Gbus write
cycle, the R_OR_WCTR bit will be written before the START_STOPBM bit.
The write to Device/Head register clears any other bits in System Control register except command and data
transfer mode field.
There are also 2 Transfer Word Count registers, 1 and 2. The mapping module maintains an internal bit to keep
track the value of DEV bit of Device/Head ATA device register. If this bit is 0, it writes the transfer word count 1,
otherwise it writes the transfer word count 2 to transfer word count register in ATA100 Core.
But it is impossible to read Transfer Word Counter register in ATA100 Core itself.
All ATA100 Core registers are 16 bits. The addresses of these registers are on 64-bit boundaries. Use only
load/store half word (16-bits) to access these registers. The ATA100 Core does not support byte access to
these registers.
User needs to specify the burst count registers as described in section 17.3.3 for variable burst length.
If the PRD_NOT_EN in DMA Command register is on, the Transfer Start Address needs to be specified.
17-4
Toshiba RISC Processor
TX4939
17
17
Related parts for TX4939XBG-400
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R
Part Number:
Description:
Toshiba Semiconductor [TOSHIBA IGBT Module Silicon N Channel IGBT]
Manufacturer:
TOSHIBA Semiconductor CORPORATION
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
TOSHIBA GTR MODULE SILICON NPN TRIPLE DIFFUSED TYPE
Manufacturer:
TOSHIBA Semiconductor CORPORATION
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
TOSHIBA GTR Module Silicon N Channel IGBT
Manufacturer:
TOSHIBA Semiconductor CORPORATION
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
TOSHIBA Intelligent Power Module Silicon N Channel IGBT
Manufacturer:
TOSHIBA Semiconductor CORPORATION
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
TOSHIBA INTELLIGENT POWER MODULE SILICON N CHANNEL LGBT
Manufacturer:
TOSHIBA Semiconductor CORPORATION
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
TOSHIBA IGBT Module Silicon N Channel IGBT
Manufacturer:
TOSHIBA Semiconductor CORPORATION
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
TOSHIBA GTR MODULE SILICON N−CHANNEL IGBT
Manufacturer:
TOSHIBA Semiconductor CORPORATION
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
TOSHIBA Intelligent Power Module Silicon N Channel IGBT
Manufacturer:
TOSHIBA Semiconductor CORPORATION
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
TOSHIBA GTR Module Silicon N Channel IGBT
Manufacturer:
TOSHIBA Semiconductor CORPORATION
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
TOSHIBA INTELLIGENT POWER MODULE
Manufacturer:
TOSHIBA Semiconductor CORPORATION
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
TOSHIBA Intelligent Power Module Silicon N Channel IGBT
Manufacturer:
TOSHIBA Semiconductor CORPORATION
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
TOSHIBA Intelligent Power Module Silicon N Channel IGBT
Manufacturer:
TOSHIBA Semiconductor CORPORATION
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
TOSHIBA IGBT Module Silicon N Channel IGBT
Manufacturer:
TOSHIBA Semiconductor CORPORATION
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
TOSHIBA Intelligent Power Module Silicon N Channel IGBT
Manufacturer:
TOSHIBA Semiconductor CORPORATION
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Toshiba Semiconductor [SILICON N CHANNEL 1GBT]
Manufacturer:
TOSHIBA Semiconductor CORPORATION
Datasheet: