CA3059 Intersil, CA3059 Datasheet - Page 27

CA3059
Manufacturer Part Number
CA3059
Description
ZERO VOLTAGE CROSSING SWITCH
Manufacturer
Intersil
Datasheet
1.CA3059.pdf
(31 pages)
Specifications of CA3059
Rohs Status
RoHS non-compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
CA3059
Manufacturer:
PHILIPS
Quantity:
563
Part Number:
CA3059
Manufacturer:
INTERSIL
Quantity:
20 000
limits the output current to approximately 3mA.
When the zero-voltage switch is connected in the DC mode,
the drive current for terminal 4 can be determined from a
curve of the external load current as a function of DC voltage
from terminals 2 and 7. Of course, if additional output current
is required, an external DC supply may be connected
between terminals 2 and 7, and resistor R
53) may be removed.
120VAC
60Hz
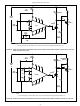
FIGURE 53. DIFFERENTIAL COMPARATOR USING THE
+
-
SENSOR
100 F
15VDC
NTC
OFF TOUCH
ON TOUCH
PLATE
PLATE
0.01 F
CA3059 INTEGRATED CIRCUIT ZERO-VOLTAGE
SWITCH
0.01 F
R
V
P
S
5.1
1M
M
1M
14
13
2
8
7
+6V
5W
5K
5
9
V
R
R
CA3059
X
10
6
6
5
3
2
44M
11
1
CA3240
CA3240
-
+
+
-
1/2
1/2
12
44M
3
X
(shown in Figure
8
FIGURE 58. ON/OFF TOUCH SWITCH
4
ANY POWER
1/2W
FACTOR Z
Application Note 6182
R
1K
G
4
G
Y
7
1
L
1
MT
MT
2
1
27
1N914
1N914
The chart below compares some of the operating
characteristics of the zero-voltage switch, when used as a
comparator, with a typical high performance commercially
available integrated circuit differential comparator.
NOTE:
Power One Shot Control
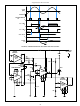
Figure 54 shows a circuit which triggers a triac for one com-
plete half cycle of either the positive or negative alternation
of the AC line voltage. In this circuit, triggering is initiated by
the push button PB-1, which produces triggering of the triac
near zero voltage even though the button is randomly
depressed during the AC cycle. The triac does not trigger
again until the button is released and again depressed. This
type of logic is required for the solenoid drive of electrically
operated stapling guns, impulse hammers, and the like,
where load current flow is required for only one complete
half cycle. Such logic can also be adapted to keyboard con-
soles in which contact bounce produces transmission of
erroneous information.
In the circuit of Figure 54, before the button is depressed,
both flip-flop outputs are in the “zero” state. Transistor Q
biased on by the output of flip-flop FF-1. The differential
comparator which is part of the zero-voltage switch is initially
Sensitivity
Switching Speed
(Rise Time)
Output Drive
Capability
1. Refer to Figure 20; R
PARAMETERS
R
42K
100 F 16VDC
36K
2
13
10
11
9
CA3059
5
2
ZERO-VOLTAGE
+6V
(TYP. VALUE)
10K
4.5V at 4mA
X
51K
R
equals 5000
7
3
SWITCH
(Note 1)
>20 s
30mV
4
8
12K
MT
G MT
2
COMPARATOR (710)
TYP. INTEGRATED
40W
120 V LIGHT
3.2V at 5.0mA
COMMON
1
CIRCUIT
120 V
AC
60Hz
90ns
2mV
G
is