MC705P6ACDWE Freescale Semiconductor, MC705P6ACDWE Datasheet - Page 33

MC705P6ACDWE
Manufacturer Part Number
MC705P6ACDWE
Description
IC MCU 176 BYTES RAM 28-SOIC
Manufacturer
Freescale Semiconductor
Series
HC05r
Datasheet
1.MC705P6ACDWE.pdf
(98 pages)
Specifications of MC705P6ACDWE
Core Processor
HC05
Core Size
8-Bit
Speed
2.1MHz
Connectivity
SIO
Peripherals
POR, WDT
Number Of I /o
21
Program Memory Size
4.5KB (4.5K x 8)
Program Memory Type
OTP
Ram Size
176 x 8
Voltage - Supply (vcc/vdd)
3 V ~ 5.5 V
Data Converters
A/D 4x8b
Oscillator Type
Internal
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 85°C
Package / Case
28-SOIC (7.5mm Width)
Processor Series
HC705P
Core
HC05
Data Bus Width
8 bit
Data Ram Size
176 B
Maximum Clock Frequency
2.1 MHz
Number Of Programmable I/os
21
Number Of Timers
1
Maximum Operating Temperature
+ 85 C
Mounting Style
SMD/SMT
Minimum Operating Temperature
- 40 C
On-chip Adc
8 bit, 4 Channel
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Eeprom Size
-
Lead Free Status / Rohs Status
Details
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
MC705P6ACDWE
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor
Quantity:
135
Part Number:
MC705P6ACDWE
Manufacturer:
FREESCALE
Quantity:
20 000
Chapter 5
Interrupts
5.1 Introduction
The MCU can be interrupted six different ways:
Interrupts cause the processor to save the register contents on the stack and to set the interrupt mask (I
bit) to prevent additional interrupts. Unlike reset, hardware interrupts do not cause the current instruction
execution to be halted, but are considered pending until the current instruction is completed.
When the current instruction is completed, the processor checks all pending hardware interrupts. If
interrupts are not masked (I bit in the condition code register is clear) and the corresponding interrupt
enable bit is set, the processor proceeds with interrupt processing. Otherwise, the next instruction is
fetched and executed. The SWI is executed the same as any other instruction, regardless of the I-bit state.
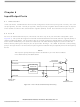
When an interrupt is to be processed, the CPU puts the register contents on the stack, sets the I bit in the
CCR, and fetches the address of the corresponding interrupt service routine from the vector table at
locations $1FF8 through $1FFF. If more than one interrupt is pending when the interrupt vector is fetched,
the interrupt with the highest vector location shown in
An RTI instruction is used to signify when the interrupt software service routine is completed. The RTI
instruction causes the CPU state to be recovered from the stack and normal processing to resume at the
next instruction that was to be executed when the interrupt took place.
events that occurs during interrupt processing.
Freescale Semiconductor
1. Non-maskable software interrupt instruction (SWI)
2. External asynchronous interrupt (IRQ)
3. Input capture interrupt (TIMER)
4. Output compare interrupt (TIMER)
5. Timer overflow interrupt (TIMER)
6. Port A interrupt (if selected via mask option register)
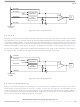
Register
TSR
TSR
TSR
N/A
N/A
N/A
Table 5-1. Vector Addresses for Interrupts and Reset
MC68HC705P6A Advance Information Data Sheet, Rev. 2.1
Name
OCF
Flag
TOF
N/A
N/A
N/A
ICF
Reset
Software
External Interrupt
Timer Input Capture
Timer Output Compare
Timer Overflow
Interrupts
Table 5-1
Interrupt
RESET
TIMER
TIMER
TIMER
will be serviced first.
CPU
SWI
IRQ
Figure 5-1
$1FFC–$1FFD
$1FFE–$1FFF
$1FFA–$1FFB
$1FF8–$1FF9
$1FF8–$1FF9
$1FF8–$1FF9
Address
Vector
shows the sequence of
33