AD9268-125EBZ Analog Devices Inc, AD9268-125EBZ Datasheet

AD9268-125EBZ
Specifications of AD9268-125EBZ
Related parts for AD9268-125EBZ
AD9268-125EBZ Summary of contents
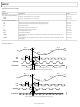
Page 1
... Pin compatibility with the AD9258, allowing a simple migration from 16 bits to 14 bits. The AD9268 is also pin compatible with the AD9251, AD9231, and of products for lower sample rate, low power applications. One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A. ...
Page 2
... AD9268 TABLE OF CONTENTS Features .............................................................................................. 1 Applications ....................................................................................... 1 Functional Block Diagram .............................................................. 1 Product Highlights ........................................................................... 1 Revision History ............................................................................... 2 General Description ......................................................................... 3 Specifications ..................................................................................... 4 ADC DC Specifications ............................................................... 4 ADC AC Specifications ................................................................. 6 Digital Specifications ................................................................... 7 Switching Specifications ................................................................ 9 Timing Specifications ................................................................ 10 Absolute Maximum Ratings .......................................................... 12 Thermal Characteristics ............................................................ 12 ESD Caution ................................................................................ 12 Pin Configurations and Function Descriptions ......................... 13 Typical Performance Characteristics ........................................... 17 Equivalent Circuits ......................................................................... 25 Theory of Operation ...
Page 3
... CMOS or LVDS. Flexible power-down options allow significant power savings, when desired. Programming for setup and control is accomplished using a 3-wire SPI-compatible serial interface. The AD9268 is available in a 64-lead LFCSP and is specified over the industrial temperature range of −40°C to +85°C. Rev Page AD9268 ...
Page 4
... Rev Page AD9268BCPZ-125 Max Min Typ Max Unit 16 Bits Guaranteed ±0.5 ±0.4 ±0.65 % FSR ±2.5 ±0.4 ±2.5 % FSR +1.3 −1.0 +1.2 LSB ±0.7 LSB ±5.1 ±5.5 LSB ± ...
Page 5
... Standby power is measured with a dc input and with the CLK pins inactive (set to AVDD or AGND). AD9268BCPZ-80 AD9268BCPZ-105 Min Typ Max Min Typ 420 450 565 485 608 582 685 45 45 0.5 2.5 0.5 Rev Page AD9268 AD9268BCPZ-125 Max Min Typ Max Unit 590 750 777 mW 800 mW 870 2.5 0.5 2.5 mW ...
Page 6
... Rev Page AD9268BCPZ-125 Typ Max Min Typ Max 78.9 78.8 78.8 77.2 78.2 76.5 76.9 77.1 75.0 75.5 78.3 78.3 78.6 76.8 77 ...
Page 7
... Full −100 Full Full 8 Full Full AGND Full 1.2 Full AGND Full −100 Full −100 Full Full 12 Rev Page AD9268 AD9268BCPZ-125 Typ Max Min Typ Max −100 −100 −99 −94 −100 −94 −94 −94 −98 −98 −94 −96 −107 −108 −107 − ...
Page 8
... AD9268 Parameter 1 LOGIC INPUT (CSB) High Level Input Voltage Low Level Input Voltage High Level Input Current Low Level Input Current Input Resistance Input Capacitance 2 LOGIC INPUT (SCLK/DFS) High Level Input Voltage Low Level Input Voltage High Level Input Current (VIN = 1.8 V) ...
Page 9
... AD9268 Max Unit 625 MHz 125 MSPS 125 MSPS ns 5 rms 4 4 +0.5 ns Cycles Cycles μ ...
Page 10
... AD9268 TIMING SPECIFICATIONS Table 5. Parameter Conditions SYNC TIMING REQUIREMENTS t SYNC to rising edge of CLK+ setup time SSYNC t SYNC to rising edge of CLK+ hold time HSYNC SPI TIMING REQUIREMENTS t Setup time between the data and the rising edge of SCLK DS t Hold time between the data and the rising edge of SCLK ...
Page 11
... N – 1 VIN t CH CLK+ CLK– t DCO DCOA/DCOB A/CH B DATA Figure 4. LVDS Mode Data Output Timing CLK+ t SSYNC SYNC Figure 5. SYNC Input Timing Requirements CLK t SKEW – – – – – – HSYNC Rev Page AD9268 – – – 8 ...
Page 12
... AD9268 ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS Table 6. Parameter 1 ELECTRICAL AVDD to AGND DRVDD to AGND VIN+A/VIN+B, VIN−A/VIN−B to AGND CLK+, CLK− to AGND SYNC to AGND VREF to AGND SENSE to AGND VCM to AGND RBIAS to AGND CSB to AGND SCLK/DFS to AGND SDIO/DCS to AGND OEB PDWN D0A/D0B through D15A/D15B to ...
Page 13
... Channel A CMOS Output Data. Output Channel A CMOS Output Data. Output Channel A CMOS Output Data. Output Channel A CMOS Output Data. Output Channel A CMOS Output Data. Output Channel A CMOS Output Data. Output Channel A CMOS Output Data. Rev Page AD9268 48 PDWN 47 OEB 46 CSB 45 SCLK/DFS 44 SDIO/DCS 43 ORA 42 ...
Page 14
... AD9268 Pin No. Mnemonic 33 D7A 34 D8A 35 D9A 36 D10A 38 D11A 39 D12A 40 D13A 41 D14A 42 D15A (MSB) 43 ORA 4 D0B (LSB) 5 D1B 6 D2B 7 D3B 8 D4B 9 D5B 11 D6B 12 D7B 13 D8B 14 D9B 15 D10B 16 D11B 17 D12B 18 D13B 20 D14B 21 D15B (MSB) 22 ORB 24 DCOA 23 DCOB SPI Control 45 SCLK/DFS 44 SDIO/DCS 46 CSB ADC Configuration ...
Page 15
... Channel A/Channel B LVDS Output Data 1—True. Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Output Data 1—Complement. Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Output Data 2—True. Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Output Data 2—Complement. Output Channel A/Channel B LVDS Output Data 3—True. Rev Page AD9268 48 PDWN 47 OEB 46 CSB 45 SCLK/DFS 44 ...
Page 16
... AD9268 Pin No. Mnemonic 11 D3− 14 D4+ 13 D4− 16 D5+ 15 D5− 18 D6+ 17 D6− 21 D7+ 20 D7− 23 D8+ 22 D8− 27 D9+ 26 D9− 30 D10+ 29 D10− 32 D11+ 31 D11− 34 D12+ 33 D12− 36 D13+ 35 D13− 39 D14+ 38 D14− 41 D15+ (MSB) 40 D15− (MSB) ...
Page 17
... MHz Figure 12. AD9268-80 Single-Tone FFT with f IN 120 100 –100 –90 = 140.1 MHz IN Figure 13. AD9268-80 Single-Tone SNR/SFDR vs. Input Amplitude (A Rev Page 80MSPS 200.3MHz @ –1dBFS SNR = 74.3dB (75.3dBFS) SFDR = 83dBc SECOND HARMONIC THIRD HARMONIC FREQUENCY (MHz) = 200.1 MHz IN 80MSPS 70.1MHz @ –6dBFS SNR = 73 ...
Page 18
... INPUT AMPLITUDE (dBFS) Figure 14. AD9268-80 Single-Tone SNR/SFDR vs. Input Amplitude ( MHz with and without Dither Enabled IN 100 100 150 INPUT FREQUENCY (MHz) Figure 15. AD9268-80 Single-Tone SNR/SFDR vs. Input Frequency (f with 2 V p-p Full Scale 105 100 SAMPLE RATE (MSPS) Figure 16. AD9268-80 Single-Tone SNR/SFDR vs. Sample Rate (f with ...
Page 19
... MHz Figure 24. AD9268-105 Single-Tone FFT with f IN 120 100 –100 – Figure 25. AD9268-105 Single-Tone SNR/SFDR vs. Input Amplitude (A = 140.1 MHz Rev Page 105MSPS 200.3MHz @ –1dBFS SNR = 74.0dB (75.0dBFS) SFDR = 79dBc SECOND THIRD HARMONIC HARMONIC FREQUENCY (MHz) = 200.3 MHz IN 105MSPS 70.1MHz @ – ...
Page 20
... MHz with and without Dither Enabled IN 100 100 150 INPUT FREQUENCY (MHz) Figure 27. AD9268-105 Single-Tone SNR/SFDR vs. Input Frequency (f with 2 V p-p Full Scale 105 SNR, CHANNEL B SFDR, CHANNEL B 100 SNR, CHANNEL A SFDR, CHANNEL 100 105 SAMPLE RATE (MSPS) Figure 28. AD9268-105 Single-Tone SNR/SFDR vs. Sample Rate (f with ...
Page 21
... Figure 35. AD9268-125 Single-Tone FFT with f = 2.4 MHz IN 0 –20 –40 –60 –80 –100 –120 –140 Figure 36. AD9268-125 Single-Tone FFT with f = 30.3 MHz IN 0 –20 –40 –60 –80 –100 –120 –140 Figure 37. AD9268-125 Single-Tone FFT with f = 70.1 MHz IN Rev Page 125MSPS 140.1MHz @ – ...
Page 22
... Figure 41. AD9268-125 Single-Tone SNR/SFDR vs. Input Amplitude (A = 70.1 MHz @ −6 dBFS Figure 42. AD9268-125 Single-Tone SNR/SFDR vs. Input Amplitude (A = 70.1 MHz @ −23 dBFS Figure 43. AD9268-125 Single Tone SNR/SFDR vs. Input Amplitude (AIN) = 70.1 MHz @ −23 dBFS IN Rev Page 120 SFDR (dBFS) 100 SNR (dBFS SFDR (dBc) 40 SNR (dBc – ...
Page 23
... INPUT FREQUENCY (MHz) Figure 44. AD9268-125 Single-Tone SNR/SFDR vs. Input Frequency (f with 2 V p-p Full Scale 95 90 SFDR (dBc SNR (dBFS 100 150 200 INPUT FREQUENCY (MHz) Figure 45. AD9268-125 Single-Tone SNR/SFDR vs. Input Frequency (fIN) with 1 V p-p Full Scale 0 – ...
Page 24
... SFDR (dBc), CHANNEL SFDR (dBc), CHANNEL A SNR (dBFS), CHANNEL B 80 SNR (dBFS), CHANNEL SAMPLE RATE (MSPS) Figure 50. AD9268-125 Single-Tone SNR/SFDR vs. Sample Rate (f with f = 70.1 MHz IN 3500 3000 2500 2000 1500 1000 500 0 OUTPUT CODE Figure 51. AD9268-125 Grounded Input Histogram 4 DITHER ENABLED DITHER DISABLED ...
Page 25
... PDWN 26kΩ Rev Page AVDD 350Ω SENSE Figure 60. Equivalent SENSE Circuit DRVDD 26kΩ 350Ω CSB Figure 61. Equivalent CSB Input Circuit AVDD VREF 6kΩ Figure 62. Equivalent VREF Circuit 350Ω 26kΩ Figure 63. Equivalent PDWN Input Circuit AD9268 ...
Page 26
... Operation to 300 MHz analog input is permitted, but it occurs at the expense of increased ADC noise and distortion. In nondiversity applications, the AD9268 can be used as a base- band or direct downconversion receiver, in which one ADC is used for I input data, and the other is used for Q input data. ...
Page 27
... AD8138, ADA4937-2, and provide excellent performance and a flexible interface to the ADC. The output common-mode voltage of the ADA4938-2 is easily set with the VCM pin of the AD9268 (see Figure 66), and the driver can be configured in a Sallen-Key filter topology to provide band limiting of the input signal. DOUT 90Ω ...
Page 28
... At input frequencies in the second Nyquist zone and above, the noise performance of most amplifiers is not adequate to achieve the true SNR performance of the AD9268. For applications in which SNR is a key parameter, differential double balun coupling is the recommended input configuration (see Figure 68). In this configuration, the input is ac-coupled, and the CML is provided to each input through a 33 Ω ...
Page 29
... The input range of the ADC always equals twice the voltage at the reference pin (VREF) for either an internal or an external reference. If the internal reference of the AD9268 is used to drive multiple converters to improve gain matching, the loading of the reference by the other converters must be considered. Figure 72 shows ADC how the internal reference voltage is affected by loading ...
Page 30
... Jitter Considerations section. Figure 75 and Figure 76 show two preferred methods for clocking the AD9268 (at clock rates up to 625 MHz). A low jitter clock source is converted from a single-ended signal to a differential signal using either an RF balun transformer. ...
Page 31
... Typical high speed ADCs use both clock edges to generate a variety of internal timing signals and result, may be sensitive to clock duty cycle. The AD9268 requires a tight tolerance on the clock duty cycle to maintain dynamic performance characteristics. The AD9268 contains a duty cycle stabilizer (DCS) that retimes the nonsampling (falling) edge, providing an internal clock signal with a nominal 50% duty cycle ...
Page 32
... AD9268 POWER DISSIPATION AND STANDBY MODE As shown in Figure 81, the power dissipated by the AD9268 varies with its sample rate. In CMOS output mode, the digital power dissipation is determined primarily by the strength of the digital drivers and the load on each output bit. The maximum DRVDD current (IDRVDD) can be calculated as IDRVDD = VDRVDD × ...
Page 33
... DCS disabled These transients can degrade converter dynamic performance. DCS enabled (default) The lowest typical conversion rate of the AD9268 is 10 MSPS. At clock rates below 10 MSPS, dynamic performance can degrade. Data Clock Output (DCO) The AD9268 provides two data clock output (DCO) signals intended for capturing the data in an external register ...
Page 34
... AD9268. BUILT-IN SELF-TEST (BIST) The BIST is a thorough test of the digital portion of the selected AD9268 signal path. When enabled, the test runs from an internal pseudorandom noise (PN) source through the digital datapath starting at the ADC block output. The BIST sequence runs for 512 cycles and stops ...
Page 35
... SERIAL PORT INTERFACE (SPI) The AD9268 serial port interface (SPI) allows the user to configure the converter for specific functions or operations through a structured register space provided inside the ADC. The SPI gives the user added flexibility and customization, depending on the application. Addresses are accessed via the serial port and can be written to or read from via the port ...
Page 36
... The pins described in Table 14 comprise the physical interface between the user programming device and the serial port of the AD9268. The SCLK pin and the CSB pin function as inputs when using the SPI. The SDIO pin is bidirectional, functioning as an input during write phases and as an output during readback ...
Page 37
... Address 0x18). If the entire address location is open (for example, Address 0x13), this address location should not be written. Default Values After the AD9268 is reset, critical registers are loaded with default values. The default values for the registers are given in the memory map register table, Table 17. Logic Levels An explanation of logic level terminology follows: • ...
Page 38
... Open (global) 0x0D Test mode Open Open (local) Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Soft reset 1 1 Soft reset 8-bit Chip ID[7:0] (AD9268 = 0x32) (default) Speed grade ID Open Open 01 = 125 MSPS 10 = 105 MSPS MSPS Open Open Open Open Open Open Open Open External ...
Page 39
... Open Open Open BIST signature[7:0] BIST signature[15:8] Open Dither Open Open enable Open Open Open Clock divider next sync only Rev Page AD9268 Default Default Bit 0 Value Notes/ Bit 1 (LSB) (Hex) Comments Open BIST 0x04 enable Open Common- 0x00 mode servo ...
Page 40
... AD9268 MEMORY MAP REGISTER DESCRIPTIONS For additional information about functions controlled in Register 0x00 to Register 0xFF, see the AN-877 Application Note, Interfacing to High Speed ADCs via SPI. Sync Control (Register 0x100) Bits[7:3]—Reserved Bit 2—Clock Divider Next Sync Only If the master sync enable bit (Address 0x100, Bit 0) and the clock ...
Page 41
... LVDS mode. This additional DRVDD current does not cause damage to the AD9268, but it should be taken into account when consid- ering the maximum DRVDD current for the part. To avoid this additional DRVDD current, the AD9268 outputs can be disabled at power-up by taking the OEB pin high ...
Page 42
... AD9268BCPZ-105 −40°C to +85°C 1 AD9268BCPZRL7-105 −40°C to +85°C 1 AD9268BCPZ-125 −40°C to +85°C AD9268BCPZRL7-125 1 −40°C to +85°C 1 AD9268-80EBZ 1 AD9268-105EBZ 1 AD9268-125EBZ RoHS Compliant Part. 9.00 BSC SQ 0.60 MAX 49 48 0.50 8.75 BSC BSC SQ 0.50 33 0.40 32 0.30 ...
Page 43
... NOTES Rev Page AD9268 ...
Page 44
... AD9268 NOTES ©2009 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved. Trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners. D08123-0-9/09(A) Rev Page ...