mc9s12c32mpb16 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc, mc9s12c32mpb16 Datasheet - Page 327
mc9s12c32mpb16
Manufacturer Part Number
mc9s12c32mpb16
Description
Hcs12 Microcontrollers
Manufacturer
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet
1.MC9S12C32MPB16.pdf
(680 pages)
- Current page: 327 of 680
- Download datasheet (4Mb)
message in its RxBG (wrong identifier, transmission errors, etc.) the actual contents of the buffer will be
over-written by the next message. The buffer will then not be shifted into the FIFO.
When the MSCAN module is transmitting, the MSCAN receives its own transmitted messages into the
background receive buffer, RxBG, but does not shift it into the receiver FIFO, generate a receive interrupt,
or acknowledge its own messages on the CAN bus. The exception to this rule is in loopback mode (see
Section 10.3.2.2, “MSCAN Control Register 1
exactly like all other incoming messages. The MSCAN receives its own transmitted messages in the event
that it loses arbitration. If arbitration is lost, the MSCAN must be prepared to become a receiver.
An overrun condition occurs when all receive message buffers in the FIFO are filled with correctly
received messages with accepted identifiers and another message is correctly received from the CAN bus
with an accepted identifier. The latter message is discarded and an error interrupt with overrun indication
is generated if enabled (see
messages while the receiver FIFO being filled, but all incoming messages are discarded. As soon as a
receive buffer in the FIFO is available again, new valid messages will be accepted.
10.4.3
The MSCAN identifier acceptance registers (see
Control Register
(ID[10:0] or ID[28:0]). Any of these bits can be marked ‘don’t care’ in the MSCAN identifier mask
registers (see
A filter hit is indicated to the application software by a set receive buffer full flag (RXF = 1) and three bits
in the CANIDAC register (see
(CANIDAC)”). These identifier hit flags (IDHIT[2:0]) clearly identify the filter section that caused the
acceptance. They simplify the application software’s task to identify the cause of the receiver interrupt. If
more than one hit occurs (two or more filters match), the lower hit has priority.
A very flexible programmable generic identifier acceptance filter has been introduced to reduce the CPU
interrupt loading. The filter is programmable to operate in four different modes (see Bosch CAN 2.0A/B
protocol specification):
Freescale Semiconductor
1. Although this mode can be used for standard identifiers, it is recommended to use the four or eight identifier acceptance
•
•
filters for standard identifiers
Two identifier acceptance filters, each to be applied to:
— The full 29 bits of the extended identifier and to the following bits of the CAN 2.0B frame:
— The 11 bits of the standard identifier plus the RTR and IDE bits of the CAN 2.0A/B messages
Four identifier acceptance filters, each to be applied to
– Remote transmission request (RTR)
– Identifier extension (IDE)
– Substitute remote request (SRR)
This mode implements two filters for a full length CAN 2.0B compliant extended identifier.
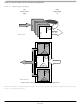
Figure 10-39
CANIDMR0–CANIDMR3) produces a filter 0 hit. Similarly, the second filter bank
(CANIDAR4–CANIDAR7, CANIDMR4–CANIDMR7) produces a filter 1 hit.
Identifier Acceptance Filter
Section 10.3.2.17, “MSCAN Identifier Mask Registers
(CANIDAC)”) define the acceptable patterns of the standard or extended identifier
shows how the first 32-bit filter bank (CANIDAR0–CANIDAR3,
Section 10.4.7.5, “Error
Section 10.3.2.12, “MSCAN Identifier Acceptance Control Register
MC9S12C-Family / MC9S12GC-Family
(CANCTL1)”) where the MSCAN treats its own messages
Chapter 10 Freescale’s Scalable Controller Area Network (S12MSCANV2)
Rev 01.23
Section 10.3.2.12, “MSCAN Identifier Acceptance
Interrupt”). The MSCAN remains able to transmit
(CANIDMR0–CANIDMR7)”).
327
1
.
Related parts for mc9s12c32mpb16
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet: