wm9709 Wolfson Microelectronics plc, wm9709 Datasheet - Page 15

wm9709
Manufacturer Part Number
wm9709
Description
Ac-link Interface Audio Dac
Manufacturer
Wolfson Microelectronics plc
Datasheet
1.WM9709.pdf
(18 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
WM9709
Manufacturer:
PHILIPS/飞利浦
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
wm9709CDS/R
Manufacturer:
WM
Quantity:
5 380
Production Data
RECOMMENDATIONS FOR 3.3V OPERATION
RECOMMENDATIONS FOR EXTERNAL FILTER
RECOMMENDATIONS FOR MINIMISING POWER UP/DOWN ‘CLICKS’
w
The WM9709 device performance with AVDD = 3.3V is shown in Electrical Characteristics.
The mid-rail reference is set to AVDD/2. The analogue full-scale output signal is 1Vrms centred at
midrail for AVDD=5V. For AVDD=3.3V, the full-scale output is 660mV rms. If 1Vrms output is
required, external gain must be increased.
For undemanding applications, the output from WM9709 may be used without an external buffer.
Typically a simple AC coupling cap of suitable value is used to remove the midrail DC pedestal from
the audio signal, with a simple RC filter used to both protect the DAC and remove any residual high
frequency RF noise which might appear at the outputs. An RC combination of series 1k resistor and
3.9nF to ground would suffice, and the resulting output impedance of 1k ohm is likely to be
acceptable in many applications.
In more demanding applications, such as DVD playback, more filtering and a lower output
impedance are often required. Due to the use of a low order sigma delta modulator on WM9709, a
second order filter may suffice. Additional filtering may not result in any significant noise reduction.
This filter is normally implemented using an active stage, which can then be used to perform the
function of increasing the output amplitude of the signal from the WM9709 from typically 1Vrms to
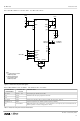
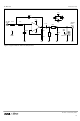
the 2Vrms often specified for consumer digital audio equipment. Figure 12 shows an example of a
typical 2
that would typically be placed between the DAC output and the filter input has been removed in order
that the DAC pedestal from the output of the DAC is maintained. This allows use of a single supply
opamp, removing the need for a negative supply in the audio subsystem. The output signals now
swing around the DC pedestal, the DC offset being removed by the AC coupling capacitor at the
filter output.
Removal of power up/down clicks is typically required in consumer electronic equipment. The
WM9709 is designed to minimise the start-up and shut down ‘click’ when power is applied or
removed or when the device is switched into or out of its reset mode of operation (RESETB state is
changed).
However, because the WM9709 DAC is followed typically by an active filter, power on/off clicks may
still occur if this filter circuit is not carefully designed, and/or some form of ‘clamp’ or ‘mute’ circuit is
not used at the output.
There are two primary concerns when attempting to minimise ‘clicks’; one is the issue of charging
the AC coupling capacitor in a controlled way and avoiding transients as the DC is established
across it. The other is avoiding ‘clicks’ when the output op-amp is powered up or down.
The first point of charging the capacitor is addressed by providing a control pin to allow the DC at the
DAC output to be ramped up or down by tying the DAC output to the CAP pin. This allows the user
to choose the external capacitor value to set the time constant. This can minimise the resultant
output transient, but it does this by giving it sub-audio characteristics, which may still cause
problems in some systems.
The second point of powering up and down the output stage opamp may or may not generate
significant ‘clicks’ depending on how the chosen opamp behaves at this time. Many opamps will
exhibit gain inversion when their supply is taken very low. At that point the output typically flips up to
the positive supply rail generating a significant output spike. If the choice of filter opamp is based on
it being well behaved under these conditions, a non-economic component choice may have to be
made.
It is recommended therefore that the whole problem be removed by use of a clamp or mute
transistor on the output of each channel, the transistor being turned on at start-up and shut down
when required.
The device could be either an appropriate series MOSFET in the signal line, or alternatively a bipolar
transistor that clamps the output to ground when the supplies are not stable. Typically low VCESAT
transistors are chosen for this function in order to minimise residual DC voltage across the clamp
device. The base or gate drive to this device will typically be the OR combination of power supply
indicator signals and mute signals from the digital controller. This allows the mute to be applied for
example in the case of damaged discs which would otherwise have caused audible noise.
nd
order filter and buffer circuit that might be used. In this case the AC coupling capacitor
PD Rev 1.3 February 2003
WM9709
15