LT1424CS8-5 Linear Technology, LT1424CS8-5 Datasheet - Page 8

LT1424CS8-5
Manufacturer Part Number
LT1424CS8-5
Description
IC SW REG ISOLATD FLYBCK 5V8SOIC
Manufacturer
Linear Technology
Type
Flybackr
Datasheet
1.LT1424IS8-5PBF.pdf
(16 pages)
Specifications of LT1424CS8-5
Internal Switch(s)
Yes
Synchronous Rectifier
No
Number Of Outputs
1
Voltage - Output
5V
Current - Output
200mA
Frequency - Switching
285kHz
Voltage - Input
2.8 ~ 20 V
Operating Temperature
0°C ~ 125°C
Mounting Type
Surface Mount
Package / Case
8-SOIC (3.9mm Width)
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
Power - Output
-
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
LT1424CS8-5
Manufacturer:
LT
Quantity:
10 000
Part Number:
LT1424CS8-5
Manufacturer:
LINEAR/凌特
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
LT1424CS8-5#PBF
Manufacturer:
LINEAR/凌特
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
LT1424CS8-5#TRPBF
Manufacturer:
LINEAR/凌特
Quantity:
20 000
LT1424-5
OPERATION
The LT1424-5 is a current mode switching regulator IC
that has been designed specifically for the isolated fly-
back topology. The special problem normally encoun-
tered in such circuits is that information relating to the
output voltage on the isolated secondary side of the
transformer must be communicated to the primary side
in order to maintain regulation. Historically, this has been
done with optoisolators or extra transformer windings.
Optoisolator circuits waste output power and the extra
components they require increase the cost and physical
volume of the power supply. Optoisolators can also
exhibit trouble due to limited dynamic response (tempo-
ral), nonlinearity, unit-to-unit variation and aging over
life. Circuits employing extra transformer windings also
exhibit deficiencies. The extra winding adds to the
transformer’s physical size and cost. Dynamic response
is often mediocre. There is usually no method for main-
taining load regulation versus load.
The LT1424-5 derives its information about the isolated
output voltage by examining the primary side flyback
pulse waveform. In this manner no optoisolator nor extra
transformer winding is required. This IC is a quantum
improvement over previous approaches because: target
output voltage is programmed by resistor ratio, regula-
tion is maintained well into discontinuous mode and
optional load compensation is available.
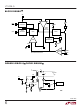
The Block Diagram shows an overall view of the system.
Many of the blocks are similar to those found in tradi-
tional designs including: internal bias regulator, oscilla-
tor, logic, current amplifier and comparator, driver and
output switch. The novel sections include a special
flyback error amplifier and a load compensation mecha-
nism. Also, due to the special dynamic requirements of
flyback control, the logic system contains additional
functionality not found in conventional designs.
The R
are application-specific thin-film resistors internal to the
LT1424-5. The capacitor connected to the R
external.
The LT1424-5 operates much the same as traditional
current mode switchers, the major difference being a
different type of error amplifier which derives its feedback
8
REF
, R
FB
and R
U
OCOMP
resistors in the Block Diagram
CCOMP
pin is
information from the flyback pulse. Due to space con-
straints, this discussion will not reiterate the basics of
current mode switcher/controllers and isolated flyback
converters. A good source of information on these topics
is LTC’s Application Note 19.
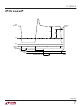
ERROR AMPLIFIER—PSEUDO DC THEORY
Please refer to the simplified diagram of the Flyback Error
Amplifier. Operation is as follows: when output switch Q4
turns off, its collector voltage rises above the V
amplitude of this flyback pulse, i.e., the difference between
it and V
The flyback voltage is then converted to a current by the
action of R
through resistor R
This is then compared to the internal bandgap reference by
the differential transistor pair Q2/Q3. The collector current
from Q2 is mirrored around and subtracted from fixed
current source I
integrates this net current to provide the control voltage to
set the current mode trip point.
The relatively high gain in the overall loop will then cause
the voltage at the R
bandgap reference V
and V
V
V
I
ESR = Total impedance of secondary circuit
N
V
V
SEC
FLBK
F
SP
FLBK
BG
V
= Ratio of Q1 I
BG
= D1 forward voltage
R
FLBK
= Transformer effective secondary-to-primary
FB
IN
= Transformer secondary current
= Internal bandgap reference
may then be expressed as:
, is given as:
=
= V
turns ratio
V
FB
=
OUT
BG
R
V
and Q1. Nearly all of this current flows
REF
BG
FXD
R
+ V
R
REF
REF
FB
REF
or,
at the V
C
F
BG
N
to form a ground-referred voltage.
+ (I
to I
. The relationship between V
resistor to be nearly equal to the
SP
1
E
SEC
C
)(ESR)
pin. An external capacitor
IN
sn14245 14245fs
rail. The
FLBK