AD7887ARM Analog Devices Inc, AD7887ARM Datasheet - Page 20

AD7887ARM
Manufacturer Part Number
AD7887ARM
Description
A/D Converter (A-D) IC
Manufacturer
Analog Devices Inc
Datasheet
1.AD7887WARMZ.pdf
(24 pages)
Specifications of AD7887ARM
Package/case
8-uSOIC
Features
+2.7 To 5.25V, 2?Channel, Power, 125kSPS
Interface Type
Serial
Number Of Bits
12
Number Of Channels
1
Mounting Type
Surface Mount
Rohs Status
RoHS non-compliant
Design Resources
Software Calibrated, 1 MHz to 8 GHz, 70 dB RF Power Measurement System Using AD8318 (CN0150)
Sampling Rate (per Second)
125k
Data Interface
DSP, MICROWIRE™, QSPI™, Serial, SPI™
Number Of Converters
1
Power Dissipation (max)
3.5mW
Voltage Supply Source
Single Supply
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 125°C
Package / Case
8-TSSOP, 8-MSOP (0.118", 3.00mm Width)
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
AD7887ARM
Manufacturer:
AD
Quantity:
5 321
Part Number:
AD7887ARM
Manufacturer:
ADI/亚德诺
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
AD7887ARMZ
Manufacturer:
ADI
Quantity:
4 130
Part Number:
AD7887ARMZ
Manufacturer:
ADI/亚德诺
Quantity:
20 000
AD7887
APPLICATION HINTS
Grounding and Layout
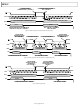
The AD7887 has very good immunity to noise on the power
supplies, as can be seen in Figure 7. However, care should still
be taken with regard to grounding and layout.
The printed circuit board that houses the AD7887 should be
designed so that the analog and digital sections are separated
and confined to certain areas of the board. This facilitates the
use of ground planes that can be easily separated. A minimum
etch technique is generally best for ground planes because it
results in the best shielding. Digital and analog ground planes
should be joined in only one place, as close as possible to the
GND pin of the AD7887. If the AD7887 is in a system where
multiple devices require AGND-to-DGND connections, the
connection should still be made at one point only, a star ground
point, which should be established as close as possible to the
AD7887.
Avoid running digital lines under the device because these will
couple noise onto the die. The analog ground plane should be
allowed to run under the AD7887 to avoid noise coupling. The
power supply lines to the AD7887 should use as large a trace as
possible to provide low impedance paths and reduce the effects
of glitches on the power supply line. Fast switching signals like
clocks should be shielded with digital ground to avoid radiating
noise to other sections of the board, and clock signals should
never be run near the analog inputs. Avoid crossover of digital
Rev. D | Page 20 of 24
and analog signals. Traces on opposite sides of the board should
run at right angles to each other. This reduces the effects of
feedthrough through the board. A microstrip technique is by far
the best approach, but it is not always possible with a double-
sided board. In this technique, the component side of the board
is dedicated to ground planes, and signals are placed on the
solder side.
Good decoupling is also important. All analog supplies should
be decoupled with 10 μF tantalum in parallel with 0.1 μF
capacitors to AGND. To achieve the best from these decoupling
components, they must be placed as close as possible to the
device, ideally right up against the device.
Evaluating the AD7887 Performance
The recommended layout for the AD7887 is outlined in the
evaluation board for the AD7887. The evaluation board
package includes a fully assembled and tested evaluation board,
documentation, and software for controlling the board from the
PC via the EVAL-CONTROL BOARD. The EVAL-CONTROL
BOARD can be used in conjunction with the AD7887
evaluation board, as well as many other Analog Devices, Inc.,
evaluation boards ending in the CB designator, to
demonstrate/evaluate the ac and dc performance of the
AD7887.
The software allows the user to perform ac (fast Fourier
transform) and dc (histogram of codes) tests on the AD7887.