TC514CPJ Microchip Technology, TC514CPJ Datasheet - Page 13

TC514CPJ
Manufacturer Part Number
TC514CPJ
Description
IC ANALOG FRONT END 17BIT 28DIP
Manufacturer
Microchip Technology
Type
Precision Analog Front Endsr
Specifications of TC514CPJ
Number Of Channels
4
Package / Case
28-DIP (0.300", 7.62mm)
Number Of Bits
17
Power (watts)
18mW
Voltage - Supply, Analog
5V
Voltage - Supply, Digital
4.5 V ~ 5.5 V
Interface Type
Serial (3-Wire)
Supply Voltage (min)
4.5 V
Supply Current
1.8 mA
Maximum Operating Temperature
+ 70 C
Minimum Operating Temperature
0 C
Mounting Style
Through Hole
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
TC514CPJ
Manufacturer:
MICROCHIP
Quantity:
1 001
6.0
6.1
The TC5XX operates with differential voltages within
the input amplifier Common mode range. The amplifier
Common mode range extends from 1.5V below
positive supply to 1.5V above negative supply. Within
this Common mode voltage range, Common mode
rejection is typically 80 dB. Full accuracy is maintained,
however, when the inputs are no less than 1.5V from
either supply.
The integrator output also follows the Common mode
voltage. The integrator output must not be allowed to
saturate. A worst-case condition exists, for example,
when a large, positive Common mode voltage, with a
near full-scale negative differential input voltage, is
applied. The negative input signal drives the integrator
positive when most of its swing has been used up by
the positive Common mode voltage. For these critical
applications, the integrator swing can be reduced. The
integrator output can swing within 0.9V of either supply
without loss of linearity.
6.2
Analog common is used as V
zero and reference de-integrate. If V
analog common, a Common mode voltage exists in the
system. This signal is rejected by the excellent CMR of
the converter. In most applications, V
fixed known voltage (i.e., power supply common). A
Common mode voltage will exist when V
connected to analog common.
6.3
The reference voltage can be anywhere within 1V of
the power supply voltage of the converter. Rollover
error is caused by the reference capacitor losing or
gaining charge due to stray capacitance on its nodes.
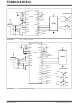
FIGURE 6-1:
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.
Comparator
Integrator
Output
Output
ANALOG SECTION
Differential Inputs (V
Analog Common
Differential Reference
(V
REF
Integrate
+
, V
Signal
REF
A. Positive Input Signal
Comparator Output.
–)
IN
return during system
IN
IN
IN
– is different from
+
– will be set at a
, V
IN
IN
–)
– is not
Reference
Deintegrate
Zero
Crossing
The difference in reference for (+) or (-) input voltages
will cause a rollover error. This error can be minimized
by using a large reference capacitor in comparison to
the stray capacitance.
6.4
The A, B unlatched logic inputs select the TC5XX
operating phase. The A, B inputs are normally driven
by a microprocessor I/O port or external logic.
6.5
By monitoring the comparator output during the fixed
signal integrate time, the input signal polarity can be
determined by the microprocessor controlling the
conversion. The comparator output is high for positive
signals and low for negative signals during the signal
integrate phase (see
During
comparator output will make a high-to-low transition as
the integrator output ramp crosses zero. The transition
is used to signal the processor that the conversion is
complete.
The internal comparator delay is 2 μs, typically.
Figure 6-1
positive and negative signal inputs. For signal inputs at
or near zero volts, however, the integrator swing is very
small. If Common mode noise is present, the
comparator can switch several times during the
beginning of the signal integrate period. To ensure that
the polarity reading is correct, the comparator output
should be read and stored at the end of the signal
integrate phase.
The comparator output is undefined during the auto-
zero phase and is used to time the integrator output
zero phase. (See Section 8.6 “Integrator Output Zero
Phase”).
Comparator
Integrator
Output
Output
Phase Control Inputs (A, B)
Comparator Output
the
Integrate
TC500/A/510/514
shows the comparator output for large
Signal
reference
B. Negative Input Signal
Figure
de-integrate
6-1).
DS21428E-page 13
Reference
De-integrate
phase,
Zero
Crossing
the