DS1350AB Maxim, DS1350AB Datasheet - Page 2

DS1350AB
Manufacturer Part Number
DS1350AB
Description
The DS1350 4096k Nonvolatile (NV) SRAMs are 4,194,304 bit, fully static, NV SRAMs organized as 524,288 words by 8 bits
Manufacturer
Maxim
Datasheet
1.DS1350AB.pdf
(10 pages)
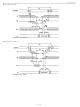
READ MODE
The DS1350 devices execute a read cycle whenever
Enable) and
(A
eight data output drivers within t
that
satisfied, then data access must be measured from the later-occurring signal (
parameter is either t
WRITE MODE
The DS1350 devices execute a write cycle whenever the
after address inputs are stable. The later-occurring falling edge of
the write cycle. The write cycle is terminated by the earlier rising edge of
must be kept valid throughout the write cycle.
time (t
during write cycles to avoid bus contention. However, if the output drivers are enabled (
active) then
DATA RETENTION MODE
The DS1350AB provides full functional capability for V
The DS1350Y provides full functional capability for V
Data is maintained in the absence of V
constantly monitor V
themselves, all inputs become “don’t care,” and all outputs become high-impedance. As V
approximately 2.7V, the power switching circuit connects the lithium energy source to RAM to retain
data. During power-up, when V
external V
after V
SYSTEM POWER MONITORING
DS1350 devices have the ability to monitor the external V
power supply condition is detected, the NV SRAMs warn a processor-based system of impending power
failure by asserting
operation during power-on transients and to allow t
BATTERY MONITORING
The DS1350 devices automatically perform periodic battery voltage monitoring on a 24-hour time
interval. Such monitoring begins within t
failure occurs.
After each 24-hour period has elapsed, the battery is connected to an internal 1MΩ test resistor for one
second. During this one second, if battery voltage falls below the battery voltage trip point (2.6V), the
battery warning output
The battery is still retested after each V
is found to be higher than 2.6V during such testing,
resumes.
0
-A
CE
18
WR
CC
) defines which of the 524,288 bytes of data is to be accessed. Valid data will be available to the
and
) before another cycle can be initiated. The
exceeds 4.75V for the DS1350AB and 4.5V for the DS1350Y.
BW
CC
WE
OE
to the RAM and disconnects the lithium energy source. Normal RAM operation can resume
OE
has an open drain output driver.
(Output Enable) are active (low). The unique address specified by the 19 address inputs
will disable the outputs in t
(Output Enable) access times are also satisfied. If
CO
CC
RST
for
. Should the supply voltage decay, the NV SRAMs automatically write protect
BW
. On power-up,
CE
is asserted. Once asserted,
or t
CC
ACC
OE
rises above approximately 2.7V, the power switching circuit connects
for
(Access Time) after the last address input signal is stable, providing
CC
OE
CC
power-up, however, even if
REC
ODW
rather than address access.
RST
without any additional support circuitry. The NV SRAMs
after V
WE
from its falling edge.
2 of 10
is held active for 200ms nominal to prevent system
REC
must return to the high state for a minimum recovery
WE
CC
to elapse.
CC
OE
CC
BW
BW
rises above V
WE
(Write Enable) is inactive (high) and
greater than 4.5V and write protects by 4.25V.
greater than 4.75V and write protects by 4.5V.
control signal should be kept inactive (high)
CC
remains active until the module is replaced.
is de-asserted and regular 24-hour testing
and
power supply. When an out-of-tolerance
RST
CE
CE
has an open drain output driver.
signals are in the active (low) state
BW
OE
or
TP
and is suspended when power
WE
is active. If the battery voltage
CE
and
CE
or
will determine the start of
CE
or
WE
access times are not
OE
. All address inputs
) and the limiting
CC
DS1350Y/AB
CE
falls below
CE
and
(Chip
OE