L6722TR STMicroelectronics, L6722TR Datasheet - Page 30
L6722TR
Manufacturer Part Number
L6722TR
Description
IC BUCK ADJ 2A TRPL 36VFQFPN
Manufacturer
STMicroelectronics
Type
Step-Down (Buck)r
Datasheet
1.L6722TR.pdf
(34 pages)
Specifications of L6722TR
Internal Switch(s)
No
Synchronous Rectifier
No
Number Of Outputs
3
Voltage - Output
Adj to 0.8V
Current - Output
2A
Frequency - Switching
100kHz
Voltage - Input
12V
Operating Temperature
0°C ~ 70°C
Mounting Type
Surface Mount
Package / Case
36-VFQFN, 36-VFQFPN
Power - Output
3.5W
Operating Temperature Range
- 40 C to + 125 C
Mounting Style
SMD/SMT
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Other names
497-5904-2
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
12 Layout guidelines
12
12.1
12.2
30/34
Layout guidelines
Since the device manages control functions and high-current drivers, layout is one of the most
important things to consider when designing such high current applications. A good layout
solution can generate a benefit in lowering power dissipation on the power paths, reducing
radiation and a proper connection between signal and power ground can optimize the
performance of the control loops.
Two kind of critical components and connections have to be considered when layouting a VR
based on L6722: power components and connections and small signal components
connections.
Power components and connections
These are the components and connections where switching and high continuous current flows
from the input to the load. The first priority when placing components has to be reserved to this
power section, minimizing the length of each connection and loop as much as possible. To
minimize noise and voltage spikes (EMI and losses) these interconnections must be a part of a
power plane and anyway realized by wide and thick copper traces: loop must be anyway
minimized. The critical components, i.e. the power transistors, must be close one to the other.
The use of multi-layer printed circuit board is recommended.
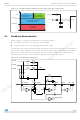
Figure 18
capacitance (C
to the power section in order to eliminate the stray inductance generated by the copper traces.
Low ESR and ESL capacitors are preferred, MLCC are suggested to be connected near the HS
drain.
Use proper VIAs number when power traces have to move between different planes on the
PCB in order to reduce both parasitic resistance and inductance. Moreover, reproducing the
same high-current trace on more than one PCB layer will reduce the parasitic resistance
associated to that connection.
Connect output bulk capacitor as near as possible to the load, minimizing parasitic inductance
and resistance associated to the copper trace also adding extra decoupling capacitors along
the way to the load when this results in being far from the bulk capacitor bank.
Gate traces must be sized according to the driver RMS current delivered to the power mosfet.
The device robustness allows managing applications with the power section far from the
controller without losing performances. Anyway, when possible, it is suggested to minimize the
distance between controller and power section.
Small signal components and connections
These are small signal components and connections to critical nodes of the application as well
as bypass capacitors for the device supply (See
and Bootstrap capacitor) close to the device and refer sensible components such as frequency
and offset setup resistors to SGND. Star grounding is suggested: connect SGND to PGND
plane in a single point to avoid that drops due to the high current delivered causes errors in the
device behavior.
shows the details of the power connections involved and the current loops. The input
IN
), or at least a portion of the total capacitance needed, has to be placed close
Figure
18). Locate the bypass capacitor (VCC
L6722