DP83932CVF25 National Semiconductor, DP83932CVF25 Datasheet
DP83932CVF25
Specifications of DP83932CVF25
Related parts for DP83932CVF25
DP83932CVF25 Summary of contents
Page 1
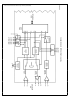
... The system allo- cates more memory resources to the SONIC by adding de- scriptors to the memory resource area The transmit buffer System Diagram TRI-STATE is a registered trademark of National Semiconductor Corporation SONIC trademark of National Semiconductor Corporation C 1995 National Semiconductor Corporation ...
Page 2
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION 1 1 IEEE 802 3 ENDEC Unit ENDEC Operation Selecting an External ENDEC 1 2 MAC Unit MAC Receive Section MAC Transmit Section 1 ...
Page 3
Functional Description The SONIC (Figure 1-1 ) consists of an encoder decoder (ENDEC) unit media access control (MAC) unit separate receive and transmit FIFOs a system buffer management engine and a user programmable system bus interface unit on ...
Page 4
Functional Description (Continued) 4 ...
Page 5
Functional Description the network The ENDEC section detects this when its colli- sion receiver detects a 10 MHz signal on the differential collision input pair The ENDEC also provides both the re- ceive and transmit clocks to the ...
Page 6
Functional Description During transmission of a packet from the SONIC the exter- nal transceiver will always loop the packet back to the SONIC The SONIC will use this to monitor the packet being transmitted The ...
Page 7
Functional Description Serializer After data has been written into the 32-byte transmit FIFO the serializer reads byte wide data from the FIFO and sends a NRZ data stream to the Manchester en- coder The rate at which data ...
Page 8
Functional Description 1 4 FIFO AND CONTROL LOGIC The SONIC incorporates two independent 32-byte FIFOs for transferring data to from the system interface and from to the network The FIFOs providing temporary storage of data free the host ...
Page 9
Functional Description 1 5 STATUS AND CONFIGURATION REGISTERS The SONIC contains a set of status control registers for conveying status and control information to from the host system The SONIC uses these registers for loading com- mands generated ...
Page 10
Functional Description 4 Program the Receive Control register with the desired re- ceive filter and the loopback mode (LB1 LB0) 5 Issue the transmit command (TXP) and enable the receiv- er (RXEN) in the Command register The SONIC ...
Page 11
Functional Description TABLE 1-1 Network Management Statistics Statistic Frames Transmitted OK Single Collision Frames Multiple Collision Frames Collision Frames Frames with Deferred Transmissions Late Collisions Excessive Collisions Excessive Deferral Internal MAC Transmit Error Frames Received OK Multicast Frames ...
Page 12
Transmit Receive IEEE 802 3 Frame Format ets from reaching a node There are three types of address formats supported by the SONIC Physical Multicast and Broadcast Physical Address The physical address is a unique ad- dress that ...
Page 13
Buffer Management 3 1 BUFFER MANAGEMENT OVERVIEW The SONIC’s buffer management scheme is based on sep- arate buffers and descriptors ( Figures 3-2 and 3-11 ) Pack- ets that are received or transmitted are placed in buffers called ...
Page 14
Buffer Management (Continued) TRANSMIT AND RECEIVE AREAS RRA Receive Resource Area RDA Receive Descriptor Area RBA Receive Buffer Area TDA Transmit Descriptor Area TBA Transmit Buffer Area BUFFER MANAGEMENT REGISTERS RSA Resource Start Area Register REA Resource End ...
Page 15
Buffer Management (Continued DESCRIPTOR DATA ALIGNMENT All fields used by descriptors (RXpkt xxx RXrsrc xxx and TXpkt xxx) are word quantities (16-bit) and must be aligned to word boundaries (A0 0) for 16-bit memory and to ...
Page 16
Buffer Management (Continued Receive Buffer Area (RBA) The SONIC stores the actual data of a received packet in the RBA The RBAs are designated by the resource descrip- tors in the RRA as described above ...
Page 17
Buffer Management (Continued Receive Descriptor Area (RDA) After the SONIC buffers a packet to memory it writes 6 words of status and control information into the RDA reads the link field to the next receive ...
Page 18
Buffer Management (Continued) All RRA registers are concatenated with the URRA register for generating the full 32-bit address The resource descriptors that the system writes to the RRA consists of four fields (1) RXrsrc buff ptr0 RXrsrc buff ...
Page 19
Buffer Management (Continued) and the buffer size to 762 words (1524 bytes) A similar example for 16-bit mode would be EOBC (1518 bytes) and the buffer size set to 760 words (1520 bytes) The buffer can be any ...
Page 20
Buffer Management (Continued) when its receive resources have been exhausted The sys- tem should respond by replenishing the resources that have been exhausted These overflow conditions (Descriptor Re- sources Exhausted Buffer Resources Exhausted and RBA Limit Exceeded) are ...
Page 21
Buffer Management (Continued) FIGURE 3-12 Transmit Descriptor Area Transmit Configuration The TXpkt config field allows the SONIC to be programmed into one of the transmit modes before each transmission At the beginning of each ...
Page 22
Buffer Management (Continued) TXpkt config to TXpkt frag size (6 accesses) For the next fragment if any it reads the next 3 fields from TXpkt frag ptr0 to TXpkt frag size (3 accesses) At the end of trans- ...
Page 23
SONIC Registers (Continued) SONIC is in software reset The CDA resides in the same 64k byte block of memory as the Receive Resource Area (RRA) and contains descriptors for loading the CAM regis- ters These descriptors are contiguous ...
Page 24
SONIC Registers (Continued Command Register 1 Data Configuration Register 2 Receive Control Register Status and Control Registers 3 Transmit Control Register 4 Interrupt Mask Register 5 Interrupt Status Register 3F Data Configuration ...
Page 25
SONIC Registers (Continued STATUS CONTROL REGISTERS This set of registers is used to convey status control infor- mation to from the host system and to control the operation of the SONIC These registers are used for ...
Page 26
SONIC Registers (Continued) RA5–RA0 Access WATCHDOG COUNTERS SILICON REVISION 28 R Note 1 These registers can only be read when the SONIC is in reset mode (RST bit in the CR is ...
Page 27
SONIC Registers (Continued REGISTER DESCRIPTION Command Register ( 0h This register (Figure 4 used for issuing commands to the SONIC These commands are issued by setting ...
Page 28
SONIC Registers (Continued REGISTER DESCRIPTION (Continued Command Register (Continued) Bit 3 RXEN RECEIVER ENABLE Setting this bit enables the receive buffer management engine to begin buffering data to memory Setting this bit resets ...
Page 29
SONIC Registers (Continued Data Configuration Register ( 1h This register (Figure 4-5) establishes the bus cycle options for reading writing data to from 16- or 32-bit memory systems During a ...
Page 30
SONIC Registers (Continued Data Configuration Register (Continued) Bits 10 SBUS SYNCHRONOUS BUS MODE The SBUS bit is used to select the mode of system bus operation when SONIC is a bus master This bit selects ...
Page 31
SONIC Registers (Continued Receive Control Register ( 2h This register is used to filter incoming packets and provide status information of accepted packets (Figure 4-6) Setting any of bits 15 ...
Page 32
SONIC Registers (Continued Receive Control Register (Continued) Bits 10 9 LB1 LB0 LOOPBACK CONTROL These encoded bits control loopback operations for MAC loopback ENDEC loopback and Transceiver loopback For proper loopback operation the CAM Address ...
Page 33
SONIC Registers (Continued Transmit Control Register ( 3h This register is used to program the SONIC’s transmit actions and provide status information after a packet has been transmit- ted (Figure ...
Page 34
SONIC Registers (Continued Transmit Control Register (Continued) Bit 9 DEF DEFERRED TRANSMISSION Indicates that the SONIC has deferred its transmission during the first attempt If subsequent collisions occur this bit is reset This bit is ...
Page 35
SONIC Registers (Continued Interrupt Mask Register ( 4h This register masks the interrupts that can be generated from the ISR (Figure 4–8) Writing a ‘‘1’’ to the bit enables the ...
Page 36
SONIC Registers (Continued Interrupt Mask Register (Continued) Bit 7 TCEN GENERAL PURPOSE TIMER COMPLETE enable 0 disable 1 enables interrupts when the general purpose timer has rolled over from 0000 0000h to FFFF FFFFh 6 ...
Page 37
SONIC Registers (Continued Interrupt Status Register ( 5h This register (Figure 4-9) indicates the source of an interrupt when the INT pin goes active Enabling the corresponding bits in the ...
Page 38
SONIC Registers (Continued Interrupt Status Register (Continued) Bit 8 TXER TRANSMIT ERROR Indicates that a packet has been transmitted with at least one of the following errors Byte count mismatch (BCM) Excessive collisions (EXC) FIFO ...
Page 39
SONIC Registers (Continued Data Configuration Register 2 ( 3Fh This register (Figure 4-10) is for enabling the extended bus interface options A hardware reset will set all bits in this ...
Page 40
SONIC Registers (Continued Transmit Registers The transmit registers described in this section are part of the User Register set The UTDA and CTDA must be initial- ized prior to issuing the transmit command (setting the ...
Page 41
SONIC Registers (Continued CAM Registers The CAM registers described in this section are part of the User Register set They are used to program the Content Addressable Memory (CAM) entries that provide address filtering of ...
Page 42
SONIC Registers (Continued General Purpose Timer The SONIC contains a 32-bit general-purpose Watchdog Timer for timing user-definable events This timer is ac- cessed by the user through two 16-bit read write registers (WT1 and WT0) ...
Page 43
Bus Interface (Continued) FIGURE 5-1 Connection Diagram (BMODE 10492 – 23 ...
Page 44
Bus Interface (Continued) FIGURE 5-2 Connection Diagram (BMODE 10492 – 24 ...
Page 45
Bus Interface (Continued PIN DESCRIPTION I input e O output e Z TRI-STATE inputs are TTL compatible e ECL ECL-like drivers for interfacing to the Attachment e Unit Interface TP Totem pole like drivers These drivers ...
Page 46
Bus Interface (Continued) Driver Symbol Direction Type NETWORK INTERFACE PINS (Continued) RXDo TP O RXDi I EXUSR0 TRI O Z RXCo TP O RXCi I EXUSR1 TRI O Z TXD TP O EXUSR3 TRI O Z TXE TP ...
Page 47
Bus Interface (Continued) Driver Symbol Direction Type NETWORK INTERFACE PINS (Continued) LBK TP O EXUSR2 TRI O Z PCOMP TRI O Z SEL I PREJ I OSCOUT TP O OSCIN I BUS INTERFACE PINS BMODE I TABLE 5-1 ...
Page 48
Bus Interface (Continued) Driver Symbol Direction Type BUS INTERFACE PINS (Continued) D31 –D0 TRI A31 –A1 TRI O Z RA5 –RA0 I AS TRI O Z ADS TRI O Z MRW TRI O Z MWR ...
Page 49
Bus Interface (Continued) Driver Symbol Direction Type BUS INTERFACE PINS (Continued SAS I SRW I SWR I DS TRI O Z DSACK0 TRI RDYi I DSACK1 TRI RDYo TP O ...
Page 50
Bus Interface (Continued) Driver Symbol Direction Type SHARED-MEMORY ACCESS PINS MREQ I SMACK TP O USER DEFINABLE PINS USR0 1 TRI POWER AND GROUND PINS VCC1 –5 VCCL TXVCC RXVCC PLLVCC GND1–6 GNDL TXGND ANGND ...
Page 51
Bus Interface (Continued) FIGURE 5-3 SONIC to Intel CPU Interface Example 10492 – 25 ...
Page 52
Bus Interface (Continued) FIGURE 5-4 SONIC to Motorola 68030 20 Interface Example 10492 – 26 ...
Page 53
Bus Interface (Continued Acquiring The Bus The SONIC requests the bus when 1) its FIFO threshold has been reached or 2) when the descriptor areas in memory (i e RRA RDA CDA and TDA) are ...
Page 54
Bus Interface (Continued) FIGURE 5-6 Bus Request Timing BMODE Block Transfers The SONIC performs block operations during all bus ac- tions thereby providing efficient transfers to memory The block cycle consists of three parts The ...
Page 55
Bus Interface (Continued Bus Status Transitions When the SONIC acquires the bus it only transfers data to from a single area in memory (i e TDA TBA RDA RBA RRA or CDA) Thus the ...
Page 56
Bus Interface (Continued Master Mode Bus Cycles In order to add additional compatibility with different bus architectures there are two other modes that affect the op- eration of the bus These modes are called the ...
Page 57
Bus Interface (Continued) FIGURE 5-8 Memory Read BMODE FIGURE 5-9 Memory Write BMODE 1 Synchronous (1 Wait-State Synchronous (1 Wait-State 10492 – 10492 – 33 ...
Page 58
Bus Interface (Continued Memory Cycle for BMODE 1 e Asynchronous Mode On the rising edge of T1 the SONIC asserts ECS to indicate that the memory cycle is starting The address (A31-A1) bus status ...
Page 59
Bus Interface (Continued) bus clocks after DSACK0 1 were sampled or 1 cycle after STERM was sampled T2 states will be repeated until DSACK0 1 or STERM are sampled properly in a low state (see note below) During ...
Page 60
Bus Interface (Continued Memory Cycle for BMODE 0 Synchronous e Mode On the rising edge of T1 the SONIC asserts ADS and ECS to indicate that the memory cycle is starting The address (A31-A1) ...
Page 61
Bus Interface (Continued Memory Cycle for BMODE 0 Asynchronous e Mode On the rising edge of T1 the SONIC asserts ADS and ECS to indicate that the memory cycle is starting The address (A31-A1) ...
Page 62
Bus Interface (Continued) During read cycles ( Figures 5-16 and 5-17 ) data (D31-D0) is latched on the rising edge at the end of T2 and DS is asserted at the falling edge of T1 For write cycles ...
Page 63
Bus Interface (Continued) FIGURE 5-20 Bus Exception (Bus Retry) Latched Bus Retry is set though the SONIC will not retry until the BR bit in the ISR (see Section has been reset and BRT is ...
Page 64
Bus Interface (Continued) FIGURE 5-21 Register Read BMODE FIGURE 5-22 Register Write BMODE 10492 – 10492 – 48 ...
Page 65
Bus Interface (Continued Slave Cycle for BMODE 0 e The system accesses the SONIC by driving SAS CS SWR and SONIC will start a slave cycle once CS and k l ...
Page 66
Bus Interface (Continued) FIGURE 5-24 Register Write BMODE FIGURE 5-25 On-Chip Memory Arbiter 10492 – 10492 – 51 ...
Page 67
Bus Interface (Continued On-Chip Memory Arbiter For applications which share the buffer memory area with the host system (shared-memory applications) the SONIC provides a fast on-chip memory arbiter for efficiently resolv- ing accesses between the ...
Page 68
Bus Interface (Continued) 13 Latched Ready Mode is disabled (DCR2) 14 PCOMP will not be asserted (DCR2) 15 Packets will be accepted (not rejected) on CAM match (DCR2) A software reset immediately terminates DMA operations and future interrupts ...
Page 69
Network Interfacing (Continued) 69 ...
Page 70
Network Interfacing (Continued) External ENDEC When EXT 1 the internal ENDEC is by- e passed and the signals are provided directly to the user Since SONIC’s on-chip ENDEC is the same as National’s DP83910 Serial Network Interface (SNI) ...
Page 71
Network Interfacing (Continued) FIGURE 6 4 Crystal Connection to the SONIC (see text) Note 1 The OSCOUT pin is not guaranteed to provide a TTL compatible logic output and should not be used to drive any external logic ...
Page 72
... AC and DC Specifications Absolute Maximum Ratings If Military Aerospace specified devices are required please contact the National Semiconductor Sales Office Distributors for availability and specifications Supply Voltage ( Input Voltage ( Output Voltage ( OUT Storage Temperature Range (T ) STG Power Dissipation (PD) Lead Temp (TL) (Soldering 10 sec ) ESD Rating ...
Page 73
AC and DC Specifications AC Characteristics BUS CLOCK TIMING Number Parameter T1 Bus Clock Low Time T2 Bus Clock High Time T3 Bus Clock Cycle Time POWER-ON RESET NON POWER-ON RESET Number Parameter T4 USR 1 0 Setup ...
Page 74
AC and DC Specifications MEMORY WRITE BMODE 0 SYNCHRONOUS MODE (one wait-state shown) e Number Parameter T9 BSCK to Address Valid Hold Time T11 BSCK to ADS Low T11b BSCK to ECS Low T12 BSCK to ADS High ...
Page 75
AC and DC Specifications MEMORY READ BMODE 0 SYNCHRONOUS MODE (one wait-state shown) e Number Parameter T9 BSCK to Address Valid Hold Time T11 BSCK to ADS Low T11b BSCK to ECS Low T12 BSCK to ADS High ...
Page 76
AC and DC Specifications MEMORY WRITE BMODE 0 ASYNCHRONOUS MODE e Number Parameter T9 BSCK to Address Valid Hold Time T11 BSCK to ADS Low T11b BSCK to ECS Low T11d BSCK to DS Low T12 BSCK to ...
Page 77
AC and DC Specifications MEMORY READ BMODE 0 ASYNCHRONOUS MODE e Number Parameter T9 BSCK to Address Valid Hold Time T11 BSCK to ADS Low T11b BSCK to ECS Low T11d BSCK to DS Low T12 BSCK to ...
Page 78
AC and DC Specifications MEMORY WRITE BMODE 1 SYNCHRONOUS MODE (one wait-state shown) e Number Parameter T9 BSCK to Address Valid Hold Time T11a BSCK to AS Low T11c BSCK to ECS Low T12a BSCK to AS High ...
Page 79
AC and DC Specifications MEMORY READ BMODE 1 SYNCHRONOUS MODE (one wait-state shown) e Number Parameter T9 BSCK to Address Valid T11a BSCK to AS Low T11c BSCK to ECS Low T12a BSCK to AS High T12c BSCK ...
Page 80
AC and DC Specifications MEMORY WRITE BMODE 1 ASYNCHRONOUS MODE e (Continued 10492 – 65 ...
Page 81
AC and DC Specifications Number Parameter T9 BSCK to Address Valid T11a BSCK to AS Low T11c BSCK to ECS Low T12a BSCK to AS High T12c BSCK to ECS High T13a BSCK to DS Low T13b BSCK ...
Page 82
AC and DC Specifications MEMORY READ BMODE 1 ASYNCHRONOUS MODE e (Continued 10492 – 66 ...
Page 83
AC and DC Specifications Number Parameter T9 BSCK to Address Valid T11a BSCK to AS Low T11c BSCK to ECS Low T12a BSCK to AS High T12c BSCK to ECS High T13a BSCK to DS Low T13b BSCK ...
Page 84
AC and DC Specifications BUS REQUEST TIMING BMODE 0 e Number Parameter T43 BSCK to HOLD High (Note 2) T44 BSCK to HOLD Low (Note 2) T45 HLDA Synchronous Setup Time to BSCK (Note 5) T46 HLDA Synchronous ...
Page 85
AC and DC Specifications BUS REQUEST TIMING BMODE 1 e Number Parameter T45a BG AS BGACK DSACK0 1 and STERM Asynchronous Setup Time to BSCK (Note 1) T51a BSCK to Address AS MRW DS ECS USR 1 0 ...
Page 86
AC and DC Specifications BUS RETRY Number Parameter T41 Bus Retry Synchronous Setup Time to BSCK (Note 3) T41a Bus Retry Asynchronous Setup Time to BSCK (Note 3) T42 Bus Retry Hold Time from BSCK (Note 2) Note ...
Page 87
AC and DC Specifications MEMORY ARBITRATION SLAVE ACCESS Number Parameter T56 CS Low Asynch Setup to BSCK (Note 2) T58 MREQ Low Asynch Setup to BSCK (Note 2) T60 MREQ or CS Valid to SMACK Low (Notes 3 ...
Page 88
AC and DC Specifications REGISTER READ BMODE 0 (Note 1) e Number Parameter T56 CS Asynch Setup to BSCK (Notes 4 6) T60a CS and SAS to SMACK Low (Notes T62 SAS Asynch Setup to ...
Page 89
AC and DC Specifications REGISTER WRITE BMODE 0 (Note 1) e Number Parameter T56 CS Asynch Setup to BSCK (Notes 4 6) T60a CS and SAS to SMACK Low (Notes T62 SAS Asynch Setup to ...
Page 90
AC and DC Specifications REGISTER READ BMODE 1 (Note 1) e (Continued 10492 – 90 ...
Page 91
AC and DC Specifications Number Parameter T56 CS Asynch Setup to BSCK (Notes 3 4) T60 CS Valid to SMACK Low (Notes T63 Register Address Setup to SAS T64 Register Address Hold from SAS T67 ...
Page 92
AC and DC Specifications REGISTER WRITE BMODE 1 (Note 1) e (Continued 10492 – 74 ...
Page 93
AC and DC Specifications Number Parameter T56 CS Asynch Setup to BSCK (Notes 3 4) T60 CS valid to SMACK Low (Notes T63 Register Address Setup to SAS T64 Register Address Hold from SAS T69 ...
Page 94
AC and DC Specifications ENDEC TRANSMIT TIMING Number Parameter T87 Transmit Clock High Time (Note 1) T88 Transmit Clock Low Time (Note 1) T89 Transmit Clock Cycle Time (Note 1) T95 Transmit Output Delay (Note 1) T96 Transmit ...
Page 95
AC and DC Specifications ENDEC RECEIVE TIMING (INTERNAL ENDEC MODE) ENDEC COLLISION TIMING Number Parameter T102 Receive Clock Duty Cycle Time (Note 1) T105 Carrier Sense On Time T106 Data Acquisition Time T107 Receive Data Output Delay T108 ...
Page 96
AC and DC Specifications ENDEC-MAC SERIAL TIMING FOR RECEPTION (EXTERNAL ENDEC MODE) Number Parameter T118 Receive Clock High Time T119 Receive Clock Low Time T120 Receive Clock Cycle Time T121 RXD Setup to RXC T122 RXD Hold from ...
Page 97
AC and DC Specifications ENDEC-MAC SERIAL TIMING FOR TRANSMISSION (COLLISION) Number Parameter T135 Collision Detect Width (Note 1) T136 Delay from Collision T137 Jam Period Note 1 tcyc transmit clock Timing Test Conditions All ...
Page 98
... Hong Kong Ltd 49) 0-180-530 85 86 13th Floor Straight Block a Ocean Centre 5 Canton Rd 49) 0-180-530 85 85 Tsimshatsui Kowloon a Tel ( 49) 0-180-532 78 32 Hong Kong a 49) 0-180-532 93 58 Tel (852) 2737-1600 a Tel ( 49) 0-180-534 16 80 Fax (852) 2736-9960 a National Semiconductor Japan Ltd Tel 81-043-299-2309 Fax 81-043-299-2408 ...