ISP1582BS,557 NXP Semiconductors, ISP1582BS,557 Datasheet
ISP1582BS,557
Specifications of ISP1582BS,557
Related parts for ISP1582BS,557
ISP1582BS,557 Summary of contents
Page 1
Dear customer, As from February 2nd 2009, ST and Ericsson have merged Ericsson Mobile Platforms and ST‐NXP Wireless into a 50/50 joint venture "ST‐Ericsson". As a result, the following changes are applicable to the attached document. ● Company name ‐ ST‐NXP Wireless is replaced with ST‐Ericsson. ● Copyright ‐ the copyright notice at the bottom of each page “© ST‐NXP Wireless 200x ‐ All rights reserved”, shall now read: “© ST‐Ericsson, 2009 ‐ All rights reserved”. ● Web site ‐ http://www.stnwireless.com is replaced with www.stericsson.com ● Contact information ‐ the list of sales offices previously obtained at http://www.stnwireless.com , is now found at www.stericsson.com under Contacts If you have any questions related to the document, please contact our nearest sales office or wired.support@stericsson.com. Thank you for your cooperation and understanding. IMPORTANT NOTICE ...
Page 2
ISP1582 Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller Rev. 08 — 22 January 2009 1. General description The ISP1582 is a cost-optimized and feature-optimized Hi-Speed Universal Serial Bus (USB) peripheral controller. It fully complies with Rev. 2.0”, supporting data transfer at high-speed (480 ...
Page 3
Supports V Supports Generic DMA (GDMA) slave mode High-speed DMA interface Fully autonomous and multi-configuration DMA operation Seven IN endpoints, seven OUT endpoints, and a fixed control IN and OUT endpoint Integrated physical multi-configuration FIFO memory Endpoints ...
Page 4
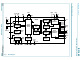
USB BUS 3.3 V 1.5 k SoftConnect RPU 2 RREF 6 HI-SPEED USB TRANSCEIVER 12 internal POWER-ON ...
Page 5
Pinning information 6.1 Pinning Fig 2. Pin configuration HVQFN56 (top view) 6.2 Pin description Table 2. [1] Symbol AGND RPU DP DM AGND RREF ISP1582_8 Product data sheet terminal 1 index area AGND 1 RPU ...
Page 6
Table 2. [1] Symbol RESET_N EOT DREQ DACK DIOR DIOW DGND INT CS_N RD_N WR_N [3] V CC(I/O) A3 ISP1582_8 Product data sheet Pin description …continued [2] Pin Type Description 7 I reset input (500 s); a ...
Page 7
Table 2. [1] Symbol DGND A7 [3] VCC1V8 DGND DATA0 DATA1 DATA2 DATA3 [3] V CC(I/O) DATA4 DATA5 DATA6 DATA7 DATA8 DATA9 DGND DATA10 DATA11 DATA12 ISP1582_8 Product data sheet Pin description …continued [2] Pin Type Description ...
Page 8
Table 2. [1] Symbol DATA13 DATA14 DATA15 [3] V CC(I/O) V BUS [3] VCC1V8 XTAL2 XTAL1 [ [ WAKEUP SUSPEND 56 GND [1] Symbol names ending with underscore N (for example, NAME_N) represent active LOW signals. ...
Page 9
Functional description The ISP1582 is a high-speed USB peripheral controller. It implements the Hi-Speed USB or the Original USB physical layer, and the packet protocol layer. It concurrently maintains USB endpoints (control IN, control OUT, and ...
Page 10
The ISP1582 operates MHz crystal oscillator. An integrated 40 multiplier generates the internal sampling clock of 480 MHz. 7.1 DMA interface, DMA handler and DMA registers The DMA block can be subdivided into two blocks: DMA handler ...
Page 11
Any A-device, including laptop, can respond to SRP. Any B-device, including a standard USB peripheral, can initiate SRP. The ISP1582 is a device that can initiate SRP. 7.6 ST-NXP Wireless high-speed transceiver 7.6.1 ST-NXP Wireless Parallel Interface ...
Page 12
ST-NXP Wireless Serial Interface Engine (SIE) The ST-NXP Wireless SIE implements the full USB protocol layer completely hardwired for speed and needs no firmware intervention. The functions of this block include: synchronization pattern recognition, parallel or serial ...
Page 13
Table 5 illustrates the behavior of output pins with V conditions. Table 3.3 V 3.3 V [1] Dead: The USB cable is plugged out, and V [2] X: Don’t care. 7.12 Interrupt 7.12.1 Interrupt output ...
Page 14
DMA Interrupt Reason register EXT_EOT INT_EOT DMA_XFER_OK DMA Interrupt Enable register IE_EXT_EOT OR IE_INT_EOT IE_DMA_XFER_OK Fig 3. Interrupt logic Interrupt Enable register IEBRESET IESOF IEDMA IEP7RX IEP7TX OR Interrupt register BRESET SOF ...
Page 15
Interrupt control Bit GLINTENA in the Mode register is a global interrupt enable or disable bit. The behavior of this bit is given in The following illustrations are only applicable for level trigger. Event A: When an interrupt event ...
Page 16
Fig 5. Resistor and electrolytic or tantalum capacitor needed for V Fig 6. Oscilloscope reading: no resistor and capacitor in the network Fig 7. Oscilloscope reading: with resistor and capacitor in the network 7.14 Power-on reset The ISP1582 requires a ...
Page 17
The RESET_N pin can either be connected to V externally controlled (by the microcontroller, ASIC, and so on). When V connected to the RESET_N pin, the internal pulse width t The power-on reset function can be explained by viewing the ...
Page 18
At the V standard electrolytic or tantalum capacitors (tested ESR output. If the ripple voltage at the input is higher than 20 mV, then use 4.7 F LOW ESR capacitors (ESR from 0.2 the USB side. ...
Page 19
Self-powered mode V Fig 11. Self-powered mode In self-powered mode, V Table 7. ISP1582 operation Normal bus operation No pull- [1] When the USB cable is removed, SoftConnect is disabled. Table 8. ISP1582 operation Clock will wake ...
Page 20
Table 10. ISP1582 operation SRP is not applicable SRP is possible 7.15.2 Bus-powered mode 3 Fig 12. Bus-powered mode In bus-powered mode (see 5 V-to-3.3 V voltage regulator. The input to the regulator is from V USB cable, ...
Page 21
Table 13. ISP1582 operation Back voltage is not measured in this mode Power loss Table 14. ISP1582 operation SRP is not applicable Power loss ISP1582_8 Product data sheet Operation truth table for back voltage compliance Power supply V CC 3.3 ...
Page 22
Register description Table 15. Register overview Name Destination Initialization registers Address device Mode device Interrupt Configuration device OTG device Interrupt Enable device Data flow registers Endpoint Index endpoints Control Function endpoint Data Port endpoint Buffer Length endpoint Buffer Status ...
Page 23
Table 15. Register overview …continued Name Destination General registers Interrupt device Chip ID device Frame Number device Scratch device Unlock Device device Test Mode PHY 8.1 Register access The ISP1582 uses a 16-bit bus access. For single-byte registers, the upper ...
Page 24
Table 16. Address register: bit allocation Bit 7 6 Symbol DEVEN Reset 0 0 Bus reset unchanged 0 Access R/W R/W Table 17. Bit Symbol 7 DEVEN DEVADDR [6:0] 8.2.2 Mode register (address: 0Ch) This register consists ...
Page 25
Table 19. Bit The status of the chip is shown in Table 20. Status of the chip V SoftConnect = on BUS On pull-up resistor on pin DP Off pull-up resistor on ...
Page 26
CDBGMOD[1:0] — Interrupts for control endpoint 0 DDBGMODIN[1:0] — Interrupts for DATA IN endpoints DDBGMODOUT[1:0] — Interrupts for DATA OUT endpoints The Debug mode settings for CDBGMOD, DDBGMODIN and DDBGMODOUT allow you to individually ...
Page 27
Table 25. Bit Symbol Description BSESS VALID 3 INIT COND 2 DISCV OTG [1] No interrupt is designed for OTG. The V pulsing (see note 2). [2] When OTG is ...
Page 28
Session Request Protocol (SRP) The ISP1582 can initiate an SRP. The B-device initiates SRP by data-line pulsing, followed by V pulsing. The ISP1582 can initiate the B-device SRP by performing the following steps: 1. Set the OTG bit to ...
Page 29
Table 26. Interrupt Enable register: bit allocation Bit 31 30 Symbol Reset - - Bus reset - - Access - - Bit 23 22 Symbol IEP6TX IEP6RX Reset 0 0 Bus reset 0 0 Access R/W R/W Bit 15 14 ...
Page 30
Table 27. Bit 8.3 Data flow registers 8.3.1 Endpoint Index register (address: 2Ch) The Endpoint Index register selects a target endpoint for register access by the microcontroller. The register consists of 1 ...
Page 31
Table 29. Bit Symbol EP0SETUP ENDPIDX[3:0] 0 DIR Table 30. Buffer name SETUP Control OUT Control IN Data OUT Data IN 8.3.2 Control Function register (address: 28h) The Control Function register performs ...
Page 32
Table 32. Bit Symbol CLBUF 3 VENDP 2 DSEN 1 STATUS 0 STALL 8.3.3 Data Port register (address: 20h) This 2-byte register provides direct access for a microcontroller to the FIFO of the indexed endpoint. ...
Page 33
Peripheral-to-host (IN endpoint): After each write action, an internal counter is auto incremented by two to the next location in the TX FIFO. When all bytes are written (FIFO byte count = endpoint MaxPacketSize), the buffer is automatically validated. The ...
Page 34
IN endpoint: When data transfer is performed in multiples of MaxPacketSize, the Buffer Length register is not significant. This register is useful only when transferring data that is not a multiple of MaxPacketSize. The following two examples demonstrate the significance ...
Page 35
Remark: For endpoint IN data transfer, firmware must ensure a 200 ns delay between writing of the data packet and reading the Buffer Status register. For endpoint OUT data transfer, firmware must also ensure a 200 ns delay between receiving ...
Page 36
Table 40. Bit The ISP1582 supports all the transfers given in Rev. 2.0”. Each programmable FIFO can independently be configured using its Endpoint MaxPacketSize register (R/W: 04h), but the total physical ...
Page 37
Table 42. Bit Symbol NOEMPKT 3 ENABLE 2 DBLBUF ENDPTYP[1:0] 8.4 DMA registers The Generic DMA (GDMA) transfer can be done by writing the proper opcode in the DMA Command register. Control ...
Page 38
In EOT-only mode, DIS_XFER_CNT must be set to logic 1. Although the DMA transfer counter can still be programmed, it will not have any effect on the DMA transfer. The DMA transfer will start once the DMA command is issued. ...
Page 39
Table 46. DMA commands Code Name Description 00h GDMA Read Generic DMA IN token transfer: Data is transferred from the external DMA bus to the internal buffer. Strobe: DIOW by the external DMA controller. 01h GDMA Write Generic DMA OUT ...
Page 40
Table 47. DMA Transfer Counter register: bit allocation Bit 31 30 Reset 0 0 Bus reset 0 0 Access R/W R/W Bit 23 22 Symbol Reset 0 0 Bus reset 0 0 Access R/W R/W Bit 15 14 Symbol Reset ...
Page 41
Table 50. Bit [1] The DREQ pin will be driven only after performing a write access to the DMA Configuration register (that is, after configuring the DMA Configuration ...
Page 42
Table 52. Bit Symbol ENDIAN[1:0] 5 EOT_POL ACK_POL 2 DREQ_POL 1 WRITE_POL 0 READ_POL 8.4.5 DMA Interrupt Reason register (address: 50h) This 2-byte register shows the source(s) of DMA interrupt. Each bit is refreshed ...
Page 43
Bit 7 6 Symbol Reset - - Bus reset - - Access - - Table 54. Bit Symbol 15 TEST3 GDMA_STOP 11 EXT_EOT 10 INT_EOT DMA_XFER_OK DMA Transfer OK: Logic 1 indicates ...
Page 44
Bit 7 6 Symbol Reset 0 0 Bus reset 0 0 Access R/W R/W 8.4.7 DMA Endpoint register (address: 58h) This 1-byte register selects a USB endpoint FIFO as a source or destination for DMA transfers. The bit allocation is ...
Page 45
Table 60. Bit 8.5 General registers 8.5.1 Interrupt register (address: 18h) The Interrupt register consists of 4 bytes. The bit allocation is given in When a bit is set in the Interrupt register, it ...
Page 46
Bit 7 6 Symbol VBUS DMA Reset 0 0 Bus reset 0 0 Access R/W R/W Table 62. Bit ...
Page 47
Chip ID register (address: 70h) This read-only register contains the chip identification and hardware version numbers. Firmware must check this information to determine functions and features supported. The register contains 3 bytes, and the bit allocation is shown in ...
Page 48
Table 66. Bit 8.5.4 Scratch register (address: 78h) This 16-bit register can be used by the firmware to save and restore information. For example, the device status before it enters the ...
Page 49
Bit 7 6 Reset Bus reset Access W W Table 70. Bit When bit PWRON in the Mode register is logic 1, the chip is powered. In such a case, you do not need to issue the ...
Page 50
Limiting values Table 73. Limiting values In accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 60134). Symbol Parameter V supply voltage CC V input/output supply voltage CC(I/O) V input voltage I I latch-up current lu V electrostatic discharge voltage ...
Page 51
Table 76. Static characteristics: digital pins +85 C; unless otherwise specified. CC(I/O) CC GND amb Symbol Parameter Input levels V LOW-level input voltage IL V HIGH-level input ...
Page 52
Table 78. Static characteristics: analog I/O pins DP and 3 GND amb Symbol Parameter Capacitance C input capacitance in Resistance Z driver output impedance for driver DRV which ...
Page 53
Table 80. Dynamic characteristics: analog I/O pins DP and 3 GND amb unless otherwise specified. Symbol Parameter t fall time ( HSF Data source ...
Page 54
T PERIOD 3.3 V differential data lines the bit duration corresponding to the USB data rate. PERIOD Fig 14. Receiver differential data jitter Fig 15. Receiver SE0 width tolerance 12.1 Register access timing Table 81. ...
Page 55
Table 81. Register access timing parameters: separate address and data buses 3 CC(I/O) CC GND Symbol Parameter t WR_N HIGH to CS_N HIGH delay WHSH t CS_N LOW to WR_N ...
Page 56
DMA timing Table 82. GDMA mode timing parameters 3 CC(I/O) CC GND Symbol Parameter T read or write cycle time cy1 t DREQ set-up time before first DACK on ...
Page 57
DREQ t su3 t su1 (1) DACK (1) DIOR or DIOW (read) DATA [ 15:0 ] (write) DATA [ 15:0 ] DREQ is asserted for every transfer. Data strobes: DIOR (read) and DACK (write). (1) Programmable polarity: shown as ...
Page 58
Programmable polarity: shown as active LOW. Remark: EOT must be valid for 36 ns (minimum) when RD_N or WR_N is active. Fig 21. EOT timing in generic processor mode 13. Application information Fig 22. Typical interface connections for generic ...
Page 59
Package outline HVQFN56: plastic thermal enhanced very thin quad flat package; no leads; 56 terminals; body 0.85 mm terminal 1 index area terminal 1 56 index area DIMENSIONS ...
Page 60
Soldering of SMD packages This text provides a very brief insight into a complex technology. A more in-depth account of soldering ICs can be found in Application Note AN10365 “Surface mount reflow soldering description”. 16.1 Introduction to soldering Soldering ...
Page 61
Reflow soldering Key characteristics in reflow soldering are: • Lead-free versus SnPb soldering; note that a lead-free reflow process usually leads to higher minimum peak temperatures (see reducing the process window • Solder paste printing issues including smearing, release, ...
Page 62
MSL: Moisture Sensitivity Level Fig 25. Temperature profiles for large and small components For further information on temperature profiles, refer to Application Note AN10365 “Surface mount reflow soldering description”. 17. Abbreviations Table 85. Acronym ACK ACPI ASIC CRC DMA ...
Page 63
Table 85. Acronym PIO PLL POR RX SE0 SIE SRP TTL TX USB 18. References [1] Universal Serial Bus Specification Rev. 2.0 [2] On-The-Go Supplement to the USB Specification Rev. 1.3 [3] Using ISP1582 composite device application with ...
Page 64
... Revision history Table 86. Revision history Document ID Release date ISP1582_8 20090122 Modifications: Globally changed NXP Semiconductors and NXP to ST-NXP Wireless. Also updated the legal text. ISP1582_7 20080922 ISP1582_6 20070920 ISP1582_5 20070201 ISP1582-04 20050104 (9397 750 14033) ISP1582-03 20040825 (9397 750 13699) ISP1582-02 ...
Page 65
Tables Table 1. Ordering information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2 Table 2. Pin description . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 66
Figures Fig 1. Block diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3 Fig 2. Pin configuration HVQFN56 (top ...
Page 67
Contents 1 General description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 2 Features . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 68
Information in this document is provided solely in connection with ST-NXP products. ST-NXP Wireless NV and its subsidiaries (“ST-NXP”) reserve the right to make changes, corrections, modifications or improvements, to this document, and the products and services described herein at ...