TJA1080ATS/2/T,112 NXP Semiconductors, TJA1080ATS/2/T,112 Datasheet
TJA1080ATS/2/T,112
Specifications of TJA1080ATS/2/T,112
Related parts for TJA1080ATS/2/T,112
TJA1080ATS/2/T,112 Summary of contents
Page 1
... The TJA1080A actively monitors the system performance using dedicated error and status information (readable by any microcontroller), as well as internal voltage and temperature monitoring. The TJA1080A supports the mode control as used in NXP Semiconductors TJA1054 (see Ref. The TJA1080A is the next step up from the TJA1080 FlexRay transceiver ...
Page 2
... NXP Semiconductors Very low EME to support unshielded cable Differential receiver with high common-mode range for ElectroMagnetic Immunity (EMI) Auto I/O level adaptation to host controller supply voltage V Can be used and 42 V powered systems Instant shut-down interface (via BGE pin) Independent power supply ramp-up for V ...
Page 3
... NXP Semiconductors 3. Ordering information Table 1. Ordering information Type number Package Name TJA1080ATS/2/T SSOP20 TJA1080A Product data sheet Description plastic shrink small outline package; 20 leads; body width 5.3 mm All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. Rev. 5 — 24 February 2011 TJA1080A FlexRay transceiver ...
Page 4
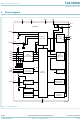
... NXP Semiconductors 4. Block diagram V 11 TRXD0 10 TRXD1 TXD 6 TXEN 8 BGE 9 STBN RXD 13 ERRN 12 RXEN V BAT 15 WAKE Fig 1. Block diagram TJA1080A Product data sheet TJA1080A SIGNAL ROUTER INPUT VOLTAGE ADAPTATION RXDINT OUTPUT VOLTAGE STATE ADAPTATION MACHINE WAKE-UP DETECTION OSCILLATOR UNDERVOLTAGE DETECTION 16 GND All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. Rev. 5 — ...
Page 5
... NXP Semiconductors 5. Pinning information 5.1 Pinning Fig 2. 5.2 Pin description Table 2. Symbol Pin INH2 INH1 TXD TXEN RXD BGE STBN TRXD1 TRXD0 RXEN ERRN V BAT WAKE GND BUF TJA1080A Product data sheet INH2 1 INH1 TXD 5 TXEN 6 RXD 7 BGE 8 9 STBN 10 TRXD1 ...
Page 6
... NXP Semiconductors 6. Functional description The block diagram of the total transceiver is illustrated in 6.1 Operating configurations 6.1.1 Node configuration In node configuration the transceiver operates as a stand-alone transceiver. The transceiver can be configured as node by connecting pins TRXD0 and TRXD1 to ground during a power-on situation (PWON flag is set). The configuration will be latched ...
Page 7
... NXP Semiconductors 6.1.3 Bus activity and idle detection The following mechanisms for activity and idle detection are valid for node and star configurations in normal power modes: If the absolute differential voltage on the bus lines is higher than |V • t det(act)(bus) LOW which results in pin RXD being released: – ...
Page 8
... NXP Semiconductors TXD BGE TXEN BP BM RXEN RXD Fig 3. Timing diagram in Normal mode node configuration STBN EN ERRN Fig 4. Timing diagram of control pins EN and STBN The state diagram in node configuration is illustrated in TJA1080A Product data sheet receive normal only standby 0.7V IO 0.3V t det(EN) ...
Page 9
... NXP Semiconductors RECEIVE ONLY 15, 25, 42 17 (1) At the first battery connection the transceiver will enter the Standby mode. Fig 5. State diagram in node configuration The state transitions are represented with numbers, which correspond with the numbers in column 3 of TJA1080A Product data sheet ...
Page 10
Table 4. State transitions forced by EN and STBN (node configuration) → → indicates the action that initiates a transaction; Transition Direction to Transition Pin from mode mode number STBN Normal Receive-only 1 H → L Go-to-sleep 2 → L ...
Page 11
Table 5. State transitions forced by a wake-up (node configuration) → → indicates the action that initiates a transaction; Transition Direction to Transition Pin from mode mode number STBN Standby Normal 16 H Receive-only 17 H Go-to-sleep 18 L Standby ...
Page 12
Table 6. State transitions forced by an undervoltage condition (node configuration) → → indicates the action that initiates a transaction; Transition from Direction to Transition mode mode number Normal Sleep 28 Sleep 29 Standby 30 Receive-only Sleep 31 Sleep 32 ...
Page 13
Table 7. State transitions forced by an undervoltage recovery (node configuration) → → indicates the action that initiates a transaction; Transition Direction to Transition Pin from mode mode number STBN Standby Normal 38 H Receive-only 39 H Sleep Normal 40 ...
Page 14
... NXP Semiconductors 6.2.1 Normal mode In Normal mode the transceiver is able to transmit and receive data via the bus lines BP and BM. The output of the normal receiver is directly connected to pin RXD. The transmitter behavior in Normal mode of operation, with no time-out present on pins TXEN and BGE and the temperature flag not set, is given in In this mode pins INH1 and INH2 are set HIGH ...
Page 15
... NXP Semiconductors 6.2.5 Sleep mode In Sleep mode the transceiver has entered a low power mode. The only difference with Standby mode is that pin INH1 is also set floating. Sleep mode is also entered if the VBAT In case of an undervoltage on pin V a positive edge on pin STBN. ...
Page 16
... NXP Semiconductors TXEN activity detected for longer than t STAR TRANSMIT INH1 = HIGH INH2 = HIGH time in star locked longer than t to(locked-sleep) from any mode if UV VCC flag is set regardless PWON flag (1) At the first battery connection the transceiver will enter the Star-standby mode. ...
Page 17
... NXP Semiconductors star transmit TRXD0 TRXD1 TXEN TXD TRXDOUT BP BM RXEN RXD TRXDOUT is a virtual signal that indicates the state of the TRXD lines. TRXDOUT HIGH means TRXD lines switched as output. TRXDOUT LOW means TRXD lines switched as input. Fig 7. Timing diagram in star configuration 6 ...
Page 18
... NXP Semiconductors 6.3.2 Star-transmit mode This mode is entered if one of the following events occur: • If the transceiver is in Star-idle mode and activity is detected on pin TXEN. • If the transceiver is in Star-idle mode and activity is detected on pins TRXD0 and TRXD1. In Star-transmit mode the transmitter is enabled and the transceiver can transmit data on the bus lines and on the TRXD lines ...
Page 19
... NXP Semiconductors 6.3.5 Star-sleep mode This mode is entered if one of the following events occur: • From any mode if an undervoltage on pin V • If the transceiver is in Star-idle mode and no activity is detected on the bus lines and pins TXEN, TRXD0 and TRXD1 for longer than t • ...
Page 20
... NXP Semiconductors 6.5 Wake-up mechanism 6.5.1 Node configuration In Sleep mode (pins INH1 and INH2 are switched off), the transceiver will enter Standby mode or Go-to-sleep mode (depending on the value at pin EN), if the wake flag is set. Consequently, pins INH1 and INH2 are switched on. ...
Page 21
... NXP Semiconductors V dif 130 ns +1500 0 V −1500 770 870 870 μs Each interruption is 130 ns. The transition time from DATA_0 to DATA_1 and from DATA_1 to DATA_0 is about 20 ns. The TJA1080A wake-up flag will be set with the following pattern: FFh, FFh, FFh, FFh, FFh, 00h, 00h, 00h, 00h, 00h, ...
Page 22
... NXP Semiconductors 6.6 Fail silent behavior In order to be fail silent, undervoltage detection and a reset mechanism for the digital state machine is implemented undervoltage is detected on pins V low power mode. This ensures a passive and defined behavior of the transmitter and receiver in case of an undervoltage detection. ...
Page 23
... NXP Semiconductors • Star configuration undervoltage is present on pin V reset) pins EN, STBN, TXD and BGE are set LOW (internally) and pin TXEN is set HIGH (internally). If the UV is present on pin V the received data on TRXD or bus lines to all other branches. 6.7 Flags 6.7.1 Local wake-up source flag The local wake-up source flag can only be set in a low power mode ...
Page 24
... NXP Semiconductors 6.7.7 Temperature high flag The temperature high flag is set if the junction temperature exceeds T power mode while pin V In node configuration the temperature high flag is reset if a negative edge is applied to pin TXEN while the junction temperature is lower than T pin V BAT ...
Page 25
... NXP Semiconductors 6.8 TRXD collision A TRXD collision is detected when both TRXD lines are LOW for more than the TRXD collision detection time (t 6.9 Status register The status register can be read out on pin ERRN by using pin EN as clock; the status bits are given in The status register is accessible if: • ...
Page 26
... NXP Semiconductors STBN EN ERRN Fig 11. Timing diagram for status bits TJA1080A Product data sheet normal d(EN-ERRN) 0. 0.3V IO All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. Rev. 5 — 24 February 2011 TJA1080A FlexRay transceiver receive only 0. det(EN) 0. 001aag896 © NXP B.V. 2011. All rights reserved. ...
Page 27
... NXP Semiconductors 7. Limiting values Table 11. Limiting values In accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 60134). All voltages are referenced to GND. Symbol Parameter V battery supply voltage BAT V supply voltage CC V supply voltage on pin V BUF V supply voltage on pin voltage on pin INH1 INH1 ...
Page 28
... NXP Semiconductors [3] According to ISO7637, test pulse 3a, class C; verified by an external test house. [4] According to ISO7637, test pulse 3b, class C; verified by an external test house. [5] In accordance with IEC 60747-1. An alternative definition of virtual junction temperature T fixed value to be used for the calculation of T temperature (T ) ...
Page 29
... NXP Semiconductors Table 13. Static characteristics All parameters are guaranteed for V − ° ° +150 bus ground; positive currents flow into the IC. Symbol Parameter Pin supply current on pin undervoltage detection uvd(VIO) voltage on pin V V undervoltage recovery uvr(VIO) voltage on pin V V undervoltage hysteresis ...
Page 30
... NXP Semiconductors Table 13. Static characteristics All parameters are guaranteed for V − ° ° +150 bus ground; positive currents flow into the IC. Symbol Parameter Pin STBN V HIGH-level input voltage IH(STBN) on pin STBN V LOW-level input voltage IL(STBN) on pin STBN I HIGH-level input current IH(STBN) ...
Page 31
... NXP Semiconductors Table 13. Static characteristics All parameters are guaranteed for V − ° ° +150 bus ground; positive currents flow into the IC. Symbol Parameter Pin RXD I HIGH-level output OH(RXD) current on pin RXD I LOW-level output OL(RXD) current on pin RXD Pin ERRN I HIGH-level output ...
Page 32
... NXP Semiconductors Table 13. Static characteristics All parameters are guaranteed for V − ° ° +150 bus ground; positive currents flow into the IC. Symbol Parameter I idle output current on o(idle)BP pin BP I idle output current on o(idle)BM pin BM V differential idle output o(idle)(dif) voltage ...
Page 33
... NXP Semiconductors Table 13. Static characteristics All parameters are guaranteed for V − ° ° +150 bus ground; positive currents flow into the IC. Symbol Parameter V DATA_1 bus cm(bus)(DATA_1) common-mode voltage ΔV bus common-mode cm(bus) voltage difference C input capacitance on pin i(BP input capacitance on pin ...
Page 34
... NXP Semiconductors Table 13. Static characteristics All parameters are guaranteed for V − ° ° +150 bus ground; positive currents flow into the IC. Symbol Parameter Power-on reset V power-on reset th(det)POR detection threshold voltage V power-on reset recovery th(rec)POR threshold voltage V power-on reset hys(POR) hysteresis voltage ...
Page 35
... NXP Semiconductors Table 14. Dynamic characteristics All parameters are guaranteed for V − ° ° +150 bus ground; positive currents flow into the IC. Symbol Parameter Δt delay time difference from bus to d(bus-TRXD) TRXD t delay time from TXEN to bus idle Normal mode d(TXEN-busidle) t delay time from TXEN to bus ...
Page 36
... NXP Semiconductors Table 14. Dynamic characteristics All parameters are guaranteed for V − ° ° +150 bus ground; positive currents flow into the IC. Symbol Parameter Star modes t idle to sleep time-out time to(idle-sleep) t transmit to locked time-out time to(tx-locked) t receive to locked time-out time to(rx-locked) t locked to sleep time-out time ...
Page 37
IO TXD 0.3V IO 0.7V IO TXEN 0.3V IO 0.7V IO BGE 0.3V IO +300 mV BP and −300 mV 0.7V IO RXEN 0.3V IO 0.7V IO RXD 0. ...
Page 38
... NXP Semiconductors Fig 13. Receiver test signal TJA1080A Product data sheet V dif (mV) 22.5 ns 400 300 −300 −400 t RXD V dif (mV) 22.5 ns 400 300 −300 −400 t RXD V is the receiver test signal. dif All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. Rev. 5 — 24 February 2011 ...
Page 39
... NXP Semiconductors 11. Test information Fig 14. Test circuit for dynamic characteristics Fig 15. Test circuit for automotive transients TJA1080A Product data sheet + 100 TJA1080A +5 V 100 BAT TJA1080A The waveforms of the applied transients are in accordance with ISO 7637, test pulses and 3b. Test conditions: Normal mode: bus idle Normal mode: bus active ...
Page 40
... NXP Semiconductors 12. Package outline SSOP20: plastic shrink small outline package; 20 leads; body width 5 pin 1 index 1 e DIMENSIONS (mm are the original dimensions) A UNIT max. 0.21 1. 0.25 0.05 1.65 Note 1. Plastic or metal protrusions of 0.2 mm maximum per side are not included. OUTLINE VERSION IEC SOT339-1 Fig 16 ...
Page 41
... NXP Semiconductors 13. Soldering of SMD packages This text provides a very brief insight into a complex technology. A more in-depth account of soldering ICs can be found in Application Note AN10365 “Surface mount reflow soldering description”. 13.1 Introduction to soldering Soldering is one of the most common methods through which packages are attached to Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs), to form electrical circuits ...
Page 42
... NXP Semiconductors 13.4 Reflow soldering Key characteristics in reflow soldering are: • Lead-free versus SnPb soldering; note that a lead-free reflow process usually leads to higher minimum peak temperatures (see reducing the process window • Solder paste printing issues including smearing, release, and adjusting the process window for a mix of large and small components on one board • ...
Page 43
... NXP Semiconductors Fig 17. Temperature profiles for large and small components For further information on temperature profiles, refer to Application Note AN10365 “Surface mount reflow soldering description”. TJA1080A Product data sheet maximum peak temperature = MSL limit, damage level temperature minimum peak temperature = minimum soldering temperature MSL: Moisture Sensitivity Level All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers ...
Page 44
... NXP Semiconductors 14. Appendix 14.1 EPL 3.0.1 requirements implemented in the TJA1080A Table 17. EPL 3.0.1 requirements implemented EPL 3.0.1 parameter - R DCLoad dBDTx10, dBDTx01 uData0_LP dBDRxai dBDActivityDetection dBDRxia uData1 − |uData0| dBDRx10, dBDRx01 dBusRx0BD, dBusRx1BD C_StarTxD, C_BDTxD - iBP ,iBM BMShortMax BPShortMax iBP ,iBM GNDShortMax ...
Page 45
... NXP Semiconductors 15. Abbreviations Table 18. Abbreviation BSS CAN CDM EMC EME EMI ESD FES HBM MM PWON TSS 16. References [1] EPL — FlexRay Communications System Electrical Physical Layer Specification Version 2.1 Rev. A, FlexRay Consortium, Dec. 2005 [2] EPL — FlexRay Communications System Electrical Physical Layer Specification Version 3 ...
Page 46
... NXP Semiconductors 17. Revision history Table 19. Revision history Document ID Release date TJA1080A v.5 20110224 • Modifications: Added FlexRay logo • Product name changed to TJA1080A • Section • Table • Table • Table • Figure • Section 14 removed; replaced with • Ref. • ...
Page 47
... In no event shall NXP Semiconductors be liable for any indirect, incidental, punitive, special or consequential damages (including - without limitation - lost profits, lost savings, business interruption, costs related to the removal or ...
Page 48
... NXP Semiconductors Export control — This document as well as the item(s) described herein may be subject to export control regulations. Export might require a prior authorization from national authorities. 18.4 Licenses NXP ICs with FlexRay functionality This NXP product contains functionality that is compliant with the FlexRay specifications ...
Page 49
... NXP Semiconductors 20. Contents 1 General description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 2 Features and benefits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 2.1 Optimized for time triggered communication systems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 2.2 Low power management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 2.3 Diagnosis (detection and signalling 2.4 Protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 2.5 Functional classes according to FlexRay electrical physical layer specification (see Ref Ordering information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3 4 Block diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4 5 Pinning information ...