AD7011ARS Analog Devices Inc, AD7011ARS Datasheet - Page 8

AD7011ARS
Manufacturer Part Number
AD7011ARS
Description
Manufacturer
Analog Devices Inc
Datasheet
1.AD7011ARS.pdf
(12 pages)
Specifications of AD7011ARS
Device Type
Modulator
Modulation Type
Quadrature
Pin Count
24
Package Type
SSOP
Lead Free Status / Rohs Status
Not Compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
AD7011ARS
Manufacturer:
ADI/亚德诺
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
AD7011ARSZ
Manufacturer:
ADI/亚德诺
Quantity:
20 000
AD7011
TERMINOLOGY
Error Vector Magnitude
This is a measure of the rms error vector introduced by the
AD7011 where signal error vector is defined as the rms devia-
tion of a transmitted symbol from its ideal position when filtered
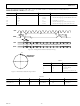
by an Ideal RRC Receive filter, as illustrated in Figure 8.
Gain Matching Between Channels
The is the gain matching between the I and Q outputs, measured
when transmitting all zeros.
Offset Vector Magnitude
This is a measure of the offset vector introduced by the AD7011
as illustrated in Figure 8. The offset vector is calculated so as to
minimize the rms error vector for each of the constellation
points.
Output Signal Range and Different Output Range
The output signal range is the output voltage swing and dc bias
level for each of the analog outputs. The different output range
is the difference between ITx and ITx for the I channel and the
difference between QTx and QTx for the Q Channel.
IS-54 Spurious Power
This is the rms sum of the spurious power measured at multiples
of 30 kHz, in a root raised cosine window of 16.4 kHz, relative
to twice the rms power in a RRC window in the 0 to 16.4 kHz
band.
Signal Vector Magnitude
This is the radius of the IQ constellation diagram as illustrated
in Figure 8.
–8–
Signal to (Noise + Distortion) Ratio
This is the measured ratio of signal to (noise + distortion) at the
output of the transmit I and Q DACs. The signal is the rms
amplitude of the fundamental. Noise is the rms sum of all non-
fundamental signals up to half the sampling frequency (f
excluding dc. The ratio is dependent upon the number of
quantization levels in the digitization process; the more levels,
the smaller the quantization noise. The theoretical signal to
(noise distortion) ratio for a sine wave is given by:
where N is the number of bits. Thus for an ideal 10-bit con-
verter, SNR = 61.96 dB.
SNR = (6.02N + 1.76) dB
VECTOR
OFFSET
Figure 8.
Q
0,0
ERROR VECTOR
SIGNAL VECTOR
I
S
REV. B
/2),