MC33991DW FREESCALE [Freescale Semiconductor, Inc], MC33991DW Datasheet

MC33991DW
Available stocks
Related parts for MC33991DW
MC33991DW Summary of contents
Page 1
... Low Sleep Mode Current • Pb-Free Packaging Designated by Suffix Code EG Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. reserves the right to change the detail specifications, as may be required, to permit improvements in the design of its products. © Freescale Semiconductor, Inc., 2006. All rights reserved. MC33991DW/R2 MCZ33991EG/R2 V PWR 33991 VPWR ...
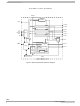
Page 2
INTERNAL BLOCK DIAGRAM VDD CS SCLK SPI SO SI RST Logic Oscillator Figure 2. 33991 Simplified Internal Block Diagram 33991 2 INTERNAL BLOCK DIAGRAM VPWR Internal Reference COS0 SIN0 COS1 H-BRIDGE & CONTROL ILIM Under & Over Voltage Over Temp ...
Page 3
Table 1. 33991 Pin Definitions Pin Number Pin Name H-Bridge Output. This is the output pin of a half bridge, designed to source or sink current. The H-Bridge 1 COS0+ pins linearly drive the sine and cosine coils of two ...
Page 4
PIN CONNECTIONS Table 1. 33991 Pin Definitions (continued) Pin Number Pin Name Reset. If the master decides to reset the device, or place it into a sleep state, the RST pin is driven RST logic 0. A ...
Page 5
Table 2. 33991 Maximum Ratings (All voltages are with respect to ground unless otherwise noted) Rating Power Supply Voltage Steady State (1) Input Pin Voltage SIN+/- COS +/- Continuous Per Output Current Storage Temperature Operating Junction Temperature Thermal Resistance (C/W) ...
Page 6
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS STATIC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS STATIC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS Table 3. Static Electrical Characteristics (Characteristics noted under conditions 4.75 V < V Characteristic POWER INPUT Supply Voltage Range Fully Operational V PWR Supply Current (Gauge 1 & 2 outputs ON, no ...
Page 7
Table 3. Static Electrical Characteristics (continued) (Characteristics noted under conditions 4.75 V < V Characteristic POWER OUTPUTS Microstep Output (measured across coil outputs) Sin0,1, ± (Cos0,1, ±) (see 33991 Pinout) Rout = 200 Ω steps 6,18 (0,12) steps 5, 7, ...
Page 8
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS STATIC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS Table 3. Static Electrical Characteristics (continued) (Characteristics noted under conditions 4.75 V < V Characteristic CONTROL I/O (9) Input Logic High Voltage (9) Input Logic Low Voltage (10) Input Logic Voltage Hysteresis Input Logic Pull ...
Page 9
Table 3. Static Electrical Characteristics (continued) (Characteristics noted under conditions 4.75 V < V Characteristic POWER OUTPUT AND CLOCK TIMINGS SIN, COS Output Turn ON delay Time (time from rising CS enabling outputs to steady state coil voltages and currents) ...
Page 10
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS STATIC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS Table 3. Static Electrical Characteristics (continued) (Characteristics noted under conditions 4.75 V < V Characteristic SPI TIMING INTERFACE Recommended Frequency of SPI Operation Falling edge Rising Edge of SCLK (Required Setup Time) ...
Page 11
RSTB RST 0.2 VDD TwRSTB TENBL CS CSB 0.7VDD Tlead 0.7VDD SCLK 0.2VDD SCLK 0.7 VDD Don’t Care SI SI 0.2VDD Figure 3. Input Timing Switching Characteristics 3.5V SCLK SO 0.2 VDD Low-to-High SO 0.7 VDD High-to-Low Figure 4. Valid ...
Page 12
SPI INTERFACE AND PROTOCOL DESCRIPTION INTRODUCTION 33991 SPI INTERFACE AND PROTOCOL DESCRIPTION The SPI interface has a full duplex, three-wire synchronous, 16-bit serial synchronous interface data transfer and four I/O lines associated with it: (SI, SO, SCLK, and CS). ...
Page 13
TIMING DESCRIPTIONS AND DIAGRAMS SCLK ...
Page 14
TIMING DESCRIPTIONS AND DIAGRAMS COMMUNICATION MEMORY MAPS MODULE MEMORY MAP Various registers of the 33991 SPI module are addressed by the three MSB of the 16-bit word received serially. Functions to be controlled include: • Individual gauge drive enabling • ...
Page 15
Nominal f=1MHz (for 8us calibration pulse) PE3—Clock Calibration Enable—This bit enables or disables the clock calibration. • Disable • Enable PE2—Oscillator Adjustment • OSC • 0. ...
Page 16
TIMING DESCRIPTIONS AND DIAGRAMS COMMUNICATION MEMORY MAPS These bits are write-only. P0 12—This bit must be transmitted as logic[0] for valid commands. P0 11: P00—Desired pointer position of Gauge 1. Pointer positions can range from 0 (000000000000) to position 4095 ...
Page 17
Table 10. The default full step time is 21.25 ms (0101). If there are two full steps per degree of pointer movement, the pointer speed is: 1/(FS×2)°. Bit D4 determines the provided blanking time immediately following ...
Page 18
TIMING DESCRIPTIONS AND DIAGRAMS COMMUNICATION MEMORY MAPS Table 13. RTZCR Full Step Time RC3 RC2 Table 14. RTZCR Accumulator Offset RC12 RC11 RC10 RC9 RC8 RC7 ...
Page 19
Gauge 1 position has not changed since the last SPI command • Gauge 1 pointer position has changed since the last SPI command ST4–Gauge 0— Movement since last SPI communication. A logic [1] on this ...
Page 20
TIMING DESCRIPTIONS AND DIAGRAMS DEVICE FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION I max + 0 I coil _ I max max + I coil max Table 16. Coil Step Value SINE Current STEP# ANGLE ...
Page 21
Table 16. Coil Step Value 20 300 -0.866 21 315 -0.707 22 330 -0.5 23 345 -0.259 Notes * Denotes Normalized Values. The motor is stepped by providing index commands at intervals. The time between steps defines the motor velocity, ...
Page 22
TIMING DESCRIPTIONS AND DIAGRAMS DEVICE FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION = 2 − ∆ − Note This means: on the nth step, the motor indexed by n positions and is accelerating steadily ...
Page 23
Table 17. Velocity Ramp (continued) Velocity Time Between Velocity Position Steps (µs) (µSteps/s) 26 615 1647.70 27 603 1680.15 28 592 1711.99 29 581 1743.24 30 571 1773.95 31 561 1804.13 32 552 1833.82 33 543 1863.04 34 534 1891.80 ...
Page 24
TIMING DESCRIPTIONS AND DIAGRAMS DEVICE FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION Table 17. Velocity Ramp (continued) Velocity Time Between Velocity Position Steps (µs) (µSteps/s) 64 385 2611.30 65 382 2631.90 66 379 2652.34 67 376 2672.62 68 374 2692.75 69 371 2712.73 70 368 ...
Page 25
For example, for the 120:1motor, the pulse would be 12 µs instead of 8 µs. The result of this slower calibration will result in the longer step times necessary to generate pointer movements meeting acceleration ...
Page 26
TIMING DESCRIPTIONS AND DIAGRAMS DEVICE FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION continue indefinitely until the RTZR bit D1 is used to stop the RTZ event. A pointer not on a full step location magnetic alignment prior to the RTZ event, may result ...
Page 27
This means, for example, all of the outputs will be disabled after a power-up or external reset, SO flag ST6 is ...
Page 28
TIMING DESCRIPTIONS AND DIAGRAMS APPLICATION INFORMATION Table 18. 33991 Setup, Configuration, & Usage Example Step # Command a. 1 PECR - Bit PE0: Gauge 0. - Bit PE1: Gauge Bit PE3: Enables Calibration Procedure. - Bit PE4: ...
Page 29
Table 18. 33991 Setup, Configuration, & Usage Example (continued) Step # Command Change the maximum velocity of the Gauge bits V8:V9 determine which gauge(s) 10 VELR will change the maximum velocity bits V7:V0 determine the maximum velocity position from the ...
Page 30
TIMING DESCRIPTIONS AND DIAGRAMS APPLICATION INFORMATION Table 18. 33991 Setup, Configuration, & Usage Example (continued) Step # Command Return the other Gauge to the zero stop. If the second gauge is driving a different 18 RTZ pointer than the first, ...
Page 31
The following example code demonstrates a typical set up configuration for a M68HC912B32 This code is intended for instructional use only. Motorola assumes no liability for use modification of this code the ...
Page 32
TIMING DESCRIPTIONS AND DIAGRAMS SAMPLE CODE /* Step 8 */ Command_Gauge(0x80,0x03); /* Step 9 */ Command_Gauge(0x10,0x00); /* Read Status until RTZ is done */ While ((status & 0x08 {Command_Gauge(0x10,0x00);} /* Step 10 */ Command_Gauge(0x23,0xFF); /* Step 11 */ ...
Page 33
Step 15 */ Command_Gauge(0x10,0x00); /* Check SO bit ST4 to see if Gauge 0 has moved */ If((status & 0x10 has moved, then keep track of position */ /* Wait until 24 steps are ...
Page 34
PACKAGE DIMENSIONS PACKAGE DIMENSIONS For the most current package revision, visit www.freescale.com and perform a keyword search using the “98A” listed below. 33991 34 PACKAGE DIMENSIONS PACKAGE DIMENSIONS DW SUFFIX EG SUFFIX (PB-FREE) 24-PIN PLASTIC PACKAGE 98ASB42344B REV. F Analog ...
Page 35
REVISION DATE DESCRIPTION OF CHANGES • Implemented Revision History page 11/2006 2.0 • Updated to current Freescale format and style • Added MCZ33991EG/R2 to the ordering Information • Removed Peak Package Reflow Temperature During Reflow (solder reflow) parameter from Maximum ...
Page 36
How to Reach Us: Home Page: www.freescale.com Web Support: http://www.freescale.com/support USA/Europe or Locations Not Listed: Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. Technical Information Center, EL516 2100 East Elliot Road Tempe, Arizona 85284 +1-800-521-6274 or +1-480-768-2130 www.freescale.com/support Europe, Middle East, and Africa: Freescale Halbleiter ...