MPC564MZP66 Freescale Semiconductor, MPC564MZP66 Datasheet - Page 349
MPC564MZP66
Manufacturer Part Number
MPC564MZP66
Description
IC MCU 512K FLASH 66MHZ 388-BGA
Manufacturer
Freescale Semiconductor
Series
MPC5xxr
Specifications of MPC564MZP66
Core Processor
PowerPC
Core Size
32-Bit
Speed
66MHz
Connectivity
CAN, EBI/EMI, SCI, SPI, UART/USART
Peripherals
POR, PWM, WDT
Number Of I /o
56
Program Memory Size
512KB (512K x 8)
Program Memory Type
FLASH
Ram Size
32K x 8
Voltage - Supply (vcc/vdd)
2.5 V ~ 2.7 V
Data Converters
A/D 32x10b
Oscillator Type
External
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 125°C
Package / Case
388-BGA
For Use With
MPC564EVB - KIT EVAL FOR MPC561/562/563/564
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
Eeprom Size
-
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
MPC564MZP66
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor
Quantity:
10 000
Company:
Part Number:
MPC564MZP66R2
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor
Quantity:
10 000
- Current page: 349 of 1420
- Download datasheet (11Mb)
9.5.2
During the data transfer phase, the data is transferred from master to slave (in write cycles) or from slave
to master (on read cycles).
During a write cycle, the master drives the data as soon as it can, but never earlier than the cycle following
the address transfer phase. The master has to take into consideration the “one dead clock cycle” switching
between drivers to avoid electrical contentions. The master can stop driving the data bus as soon as it
samples the TA line asserted on the rising edge of the CLKOUT.
During a read cycle, the master accepts the data bus contents as valid at the rising edge of the CLKOUT
in which the TA signal is sampled/asserted.
9.5.2.1
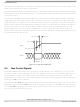
The basic read cycle begins with bus arbitration, followed by the address transfer, then the data transfer.
The handshakes illustrated in the following flow and timing figures
Figure
Freescale Semiconductor
9-6) are applicable to the fixed transaction protocol.
Single Beat Transfer
Single Beat Read Flow
4. Assert transfer start (TS)
3. Assert bus busy (BB) if no other master is driving bus
5. Drive address and attributes
2. Receive bus grant (BG) from arbiter
1. Request bus (BR)
Figure 9-4. Basic Flow Diagram of a Single Beat Read Cycle
Master
MPC561/MPC563 Reference Manual, Rev. 1.2
1. Receive address
2. Return data
3. Assert transfer acknowledge (TA)
(Figure
Slave
9-4,
Figure
External Bus Interface
9-5, and
9-9
Related parts for MPC564MZP66
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
MPC5 1K0 5%
Manufacturer:
TE Connectivity
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MPC5 500R 5%
Manufacturer:
TE Connectivity
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MPC5 5K0 5%
Manufacturer:
Tyco Electronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MPC5 5R0 5%
Manufacturer:
Tyco Electronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MPC5 50K 5%
Manufacturer:
Tyco Electronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MPC5 1R0 5%
Manufacturer:
Tyco Electronics
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet: