MC68HC16Z1CFC16 Freescale Semiconductor, MC68HC16Z1CFC16 Datasheet - Page 204
MC68HC16Z1CFC16
Manufacturer Part Number
MC68HC16Z1CFC16
Description
IC MPU 1K RAM 16MHZ 132-PQFP
Manufacturer
Freescale Semiconductor
Series
HC16r
Specifications of MC68HC16Z1CFC16
Core Processor
CPU16
Core Size
16-Bit
Speed
16MHz
Connectivity
EBI/EMI, SCI, SPI
Peripherals
POR, PWM, WDT
Number Of I /o
16
Program Memory Type
ROMless
Ram Size
1K x 8
Voltage - Supply (vcc/vdd)
2.7 V ~ 5.5 V
Data Converters
A/D 8x10b
Oscillator Type
Internal
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 85°C
Package / Case
132-QFP
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
Eeprom Size
-
Program Memory Size
-
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
MC68HC16Z1CFC16
Manufacturer:
FREESCALE
Quantity:
1 410
Company:
Part Number:
MC68HC16Z1CFC16
Manufacturer:
FREESCALE
Quantity:
5 530
Company:
Part Number:
MC68HC16Z1CFC16
Manufacturer:
MOT
Quantity:
5 510
Company:
Part Number:
MC68HC16Z1CFC16
Manufacturer:
MOTOROLA
Quantity:
1
Part Number:
MC68HC16Z1CFC16
Manufacturer:
MOTOROLA/摩托罗拉
Quantity:
20 000
- Current page: 204 of 500
- Download datasheet (6Mb)
8.8.4 Accommodating Positive/Negative Stress Conditions
8-18
Other suggestions for PCB layout in which the ADC is employed include the following:
Positive or negative stress refers to conditions which exceed nominally defined oper-
ating limits. Examples include applying a voltage exceeding the normal limit on an
input (for example, voltages outside of the suggested supply/reference ranges) or
causing currents into or out of the pin which exceed normal limits. ADC specific con-
siderations are voltages greater than V
input which cause excessive currents into or out of the input. Refer to
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Both stress conditions can potentially disrupt conversion results on neighboring inputs.
Parasitic devices, associated with CMOS processes, can cause an immediate disrup-
tive influence on neighboring pins. Common examples of parasitic devices are diodes
to substrate and bipolar devices with the base terminal tied to substrate (V
ground). Under stress conditions, current introduced on an adjacent pin can cause er-
rors on adjacent channels by developing a voltage drop across the adjacent external
channel source impedances.
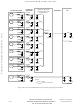
Figure 8-7
stress conditions. Positive stress conditions do not activate a similar parasitic device.
• The analog ground must be low impedance to all analog ground points in the cir-
• Bypass capacitors should be as close to the power pins as possible.
• The analog ground should be isolated from the digital ground. This can be done
• Non-minimum traces should be utilized for connecting bypass capacitors and
• Minimum distance for trace runs when possible.
cuit.
by cutting a separate ground plane for the analog ground.
filters to their corresponding ground/power points.
This star-point scheme still requires adequate grounding for digital
and analog subsystems in addition to the star-point ground.
shows an active parasitic bipolar when an input pin is subjected to negative
Figure 8-7 Input Pin Subjected to Negative Stress
VDD
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
For More Information On This Product,
NEGATIVE
ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTER
VOLTAGE
STRESS
+
Go to: www.freescale.com
R
R
ADJACENT
STRESS
on exact magnitudes.
10K
DDA
NOTE
, V
I
OUT
I
IN
RH
PARASITIC
or less than V
DEVICE
PIN UNDER
ADJACENT
STRESS
PINS
SSA
applied to an analog
M68HC16 Z SERIES
USER’S MANUAL
APPENDIX A
ADC PAR STRESS CONN
SSI
/V
SSA
Related parts for MC68HC16Z1CFC16
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet: