MC145574APB Freescale Semiconductor, MC145574APB Datasheet - Page 27
MC145574APB
Manufacturer Part Number
MC145574APB
Description
IC TRANSCEIVER ISDN 32-LQFP
Manufacturer
Freescale Semiconductor
Type
Transceiverr
Specifications of MC145574APB
Voltage - Supply
4.75 V ~ 5.25 V
Mounting Type
Surface Mount
Package / Case
32-LQFP
Number Of Line Interfaces
1
Control Interface
HDLC
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
Number Of Drivers/receivers
-
Protocol
-
Lead Free Status / Rohs Status
Not Compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
MC145574APB
Manufacturer:
ON
Quantity:
1 500
Company:
Part Number:
MC145574APB
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor
Quantity:
10 000
Part Number:
MC145574APB
Manufacturer:
MOTOROLA/摩托罗拉
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
MC145574APBR2
Manufacturer:
MOTOROLA
Quantity:
742
Part Number:
MC145574APBR2
Manufacturer:
MOTOROLA/摩托罗拉
Quantity:
20 000
MOTOROLA
4.1
4.2
INTRODUCTION
The Interchip Digital Link (IDL2) of the MC145574 is backwards compatible with the IDL of the
MC145474/75 S/T transceiver of first generation. In addition to the standard operating mode, this en-
hanced interface features new modes that are programmable through the SCP.
The IDL2 is a four–wire interface used for full–duplex communication between ICs on the board level.
The interface consists of a transmit path, a receive path, an associated clock, and a sync signal. These
signals are known as D out , D in , DCL, and FSC, respectively. The clock determines the rate of exchange
of data in both the transmit and receive directions, and the sync signal controls when this exchange
is to take place. Three channels of data are exchanged every 8 kHz. These channels consist of two
64 kbps B channels and one 16 kbps D channel used for full–duplex communication between the
NT and TE.
There are two modes of operation for an IDL2 device: IDL2 master and IDL2 slave. If an IDL2 device
is configured as an IDL2 master, then FSC and DCL are outputs from the device. Conversely, if an
IDL2 device is configured as an IDL2 slave, then FSC and DCL are inputs to the device. Ordinarily
the MC145574 should be configured as an IDL2 slave when acting as an NT, and as an IDL2 master
when acting as a TE. The exception to this rule is the option to configure the NT as an IDL2 master.
The TE configured MC145574 also features the new option of operating in the IDL2 slave mode. These
operation modes are described in Section 4.3.
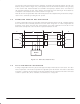
SIGNAL DESCRIPTION
There are six pins associated with the IDL2 interface.
FSC/FSR
This pin is normally FSC and is an input/output pin to which all serial interface events are synchronized.
This pin is periodic at 8 kHz. In the master mode, the pin is an output and is either derived from the
S/T frame or from the XTAL. In the slave mode, this pin is an input.
FSC can be reconfigured through the SCP to be FSR. In this mode, the IDL2 operates with two indepen-
dent frame syncs, one for the Tx direction (FST) and one for the Rx direction (FSR). FSR is bidirectional,
the direction depending on whether the IDL2 is a master or a slave. See Register OR7 description.
DCL
This is an input/output pin that provides the clock to the serial interface. In the master mode, this pin
is an output. In the slave mode, this pin is an input. The clock is continuous and the edges are synchro-
nous with the frame sync.
When DCL is an output, the clock rate can be programmed through the SCP to be 2.56 MHz,
2.048 MHz, 1.536 MHz, or 512 kHz. When DCL is an input, the clock rate can be between 512 kHz
and 4096 kHz (DCL should be a multiple of FSC.) Selection of the clock frequency is accomplished
in the same manner as used in MC145474, through the bits BR7(2) and BR13(5). See Table 4–1
for IDL2 clock speeds.
THE INTERCHIP DIGITAL LINK
MC145574
4
4–1