ST72334N4 STMicroelectronics, ST72334N4 Datasheet - Page 54

ST72334N4
Manufacturer Part Number
ST72334N4
Description
8-BIT MCU WITH SINGLE VOLTAGE FLASH MEMORY,ADC, 16-BIT TIMERS, SPI, SCI INTERFACES
Manufacturer
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet
1.ST72124J2.pdf
(153 pages)
Specifications of ST72334N4
Clock Sources
crystal/ceramic resonator oscillators or RC oscillators, external clock, backup Clock Security System
4 Power Saving Modes
Halt, Active-Halt, Wait and Slow
Two 16-bit Timers With
2 input captures (only one on timer A), 2 output compares (only one on timer A), External clock input on timer A, PWM and Pulse generator modes
- Current page: 54 of 153
- Download datasheet (3Mb)
ST72334J/N, ST72314J/N, ST72124J
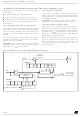
14.3 16-BIT TIMER
14.3.1 Introduction
The timer consists of a 16-bit free-running counter
driven by a programmable prescaler.
It may be used for a variety of purposes, including
measuring the pulse lengths of up to two input sig-
nals ( input capture ) or generating up to two output
waveforms ( output compare and PWM ).
Pulse lengths and waveform periods can be mod-
ulated from a few microseconds to several milli-
seconds using the timer prescaler and the CPU
clock prescaler.
Some ST7 devices have two on-chip 16-bit timers.
They are completely independent, and do not
share any resources. They are synchronized after
a MCU reset as long as the timer clock frequen-
cies are not modified.
This description covers one or two 16-bit timers. In
ST7 devices with two timers, register names are
prefixed with TA (Timer A) or TB (Timer B).
14.3.2 Main Features
The Block Diagram is shown in
*Note: Some timer pins may not be available (not
bonded) in some ST7 devices. Refer to the device
pin out description.
When reading an input signal on a non-bonded
pin, the value will always be ‘1’.
54/153
– 2 dedicated 16-bit registers
– 2 dedicated programmable signals
– 2 dedicated status flags
– 1 dedicated maskable interrupt
– 2 dedicated 16-bit registers
– 2 dedicated active edge selection signals
– 2 dedicated status flags
– 1 dedicated maskable interrupt
Programmable prescaler: f
Overflow status flag and maskable interrupt
External clock input (must be at least 4 times
slower than the CPU clock speed) with the choice
of active edge
Output compare functions with:
Input capture functions with:
Pulse Width Modulation mode (PWM)
One Pulse mode
5 alternate functions on I/O ports (ICAP1, ICAP2,
OCMP1, OCMP2, EXTCLK)*
CPU
Figure
divided by 2, 4 or 8.
31.
Alternate Counter Register (ACR)
These two read-only 16-bit registers contain the
same value but with the difference that reading the
ACLR register does not clear the TOF bit (Timer
overflow flag), located in the Status register (SR).
(See note at the end of paragraph titled 16-bit read
sequence).
Writing in the CLR register or ACLR register resets
the free running counter to the FFFCh value.
Both counters have a reset value of FFFCh (this is
the only value which is reloaded in the 16-bit tim-
er). The reset value of both counters is also
FFFCh in One Pulse mode and PWM mode.
The timer clock depends on the clock control bits
of the CR2 register, as illustrated in
Control
peats every 131072, 262144 or 524288 CPU clock
cycles depending on the CC[1:0] bits.
The timer frequency can be f
or an external frequency.
14.3.3 Functional Description
14.3.3.1 Counter
The main block of the Programmable Timer is a
16-bit free running upcounter and its associated
16-bit registers. The 16-bit registers are made up
of two 8-bit registers called high & low.
Counter Register (CR):
– Counter High Register (CHR) is the most sig-
– Counter Low Register (CLR) is the least sig-
– Alternate Counter High Register (ACHR) is the
– Alternate Counter Low Register (ACLR) is the
nificant byte (MS Byte).
nificant byte (LS Byte).
most significant byte (MS Byte).
least significant byte (LS Byte).
Bits. The value in the counter register re-
CPU
/2, f
Table 14 Clock
CPU
/4, f
CPU
/8
Related parts for ST72334N4
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
STMicroelectronics [RIPPLE-CARRY BINARY COUNTER/DIVIDERS]
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
STMicroelectronics [LIQUID-CRYSTAL DISPLAY DRIVERS]
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
BOARD EVAL FOR MEMS SENSORS
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
NPN TRANSISTOR POWER MODULE
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
TURBOSWITCH ULTRA-FAST HIGH VOLTAGE DIODE
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
DIODE / SCR MODULE
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
DIODE / SCR MODULE
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Search -----> STE16N100
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Search ---> STE53NA50
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
NPN Transistor Power Module
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
DIODE / SCR MODULE
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet: