mc56f8335 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc, mc56f8335 Datasheet - Page 117
mc56f8335
Manufacturer Part Number
mc56f8335
Description
16-bit Digital Signal Controller
Manufacturer
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet
1.MC56F8335.pdf
(160 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
mc56f8335MFGE
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor
Quantity:
135
Company:
Part Number:
mc56f8335MFGE
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor
Quantity:
10 000
Company:
Part Number:
mc56f8335VFGE
Manufacturer:
MOTOLOLA
Quantity:
621
Company:
Part Number:
mc56f8335VFGE
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor
Quantity:
10 000
Part Number:
mc56f8335VFGE
Manufacturer:
FREESCALE
Quantity:
20 000
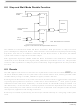
Part 7 Security Features
The 56F8335/56F8135 offer security features intended to prevent unauthorized users from reading the
contents of the Flash Memory (FM) array. The Flash security consists of several hardware interlocks that
block the means by which an unauthorized user could gain access to the Flash array.
However, part of the security must lie with the user’s code. An extreme example would be user’s code that
dumps the contents of the internal program, as this code would defeat the purpose of security. At the same
time, the user may also wish to put a “backdoor” in his program. As an example, the user downloads a
security key through the SCI, allowing access to a programming routine that updates parameters stored in
another section of the Flash.
7.1 Operation with Security Enabled
Once the user has programmed the Flash with his application code, the device can be secured by
programming the security bytes located in the FM configuration field, which occupies a portion of the FM
array. These non-volatile bytes will keep the part secured through reset and through power-down of the
device. Only two bytes within this field are used to enable or disable security. Refer to the Flash Memory
section in the 56F8300 Peripheral User Manual for the state of the security bytes and the resulting state
of security. When Flash security mode is enabled in accordance with the method described in the Flash
Memory module specification, the device will disable the core EOnCE debug capabilities. Normal
program execution is otherwise unaffected.
7.2 Flash Access Blocking Mechanisms
The 56F8335/56F8135 have several operating functional and test modes. Effective Flash security must
address operating mode selection and anticipate modes in which the on-chip Flash can be compromised
and read without explicit user permission. Methods to block these are outlined in the next subsections.
7.2.1
At boot time, the SIM determines in which functional modes the device will operate. These are:
When Flash security is enabled as described in the Flash Memory module specification, the device will
disable the EOnCE debug interface.
7.2.2
On-chip Flash can be read by issuing commands across the EOnCE port, which is the debug interface for
the 56800E core. The TRST, TCLK, TMS, TDO, and TDI pins comprise a JTAG interface onto which the
EOnCE port functionality is mapped. When the device boots, the chip-level JTAG TAP (Test Access Port)
is active and provides the chip’s boundary scan capability and access to the ID register.
Proper implementation of Flash security requires that no access to the EOnCE port is provided when
security is enabled. The 56800E core has an input which disables reading of internal memory via the
JTAG/EOnCE. The FM sets this input at reset to a value determined by the contents of the FM security
bytes.
Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
•
•
Unsecured Mode
Secure Mode (EOnCE disabled)
Forced Operating Mode Selection
Disabling EOnCE Access
56F8335 Technical Data, Rev. 5
Operation with Security Enabled
117