IPR-FIR Altera, IPR-FIR Datasheet - Page 37
IPR-FIR
Manufacturer Part Number
IPR-FIR
Description
IP CORE Renewal Of IP-FIR
Manufacturer
Altera
Type
MegaCorer
Specifications of IPR-FIR
Software Application
IP CORE, DSP Filters And Transforms
Supported Families
Arria GX, Arria II GX, Cyclone, HardCopy, Stratix
Core Architecture
FPGA
Core Sub-architecture
Arria, Cyclone, Stratix
Rohs Compliant
NA
Function
Finite Impulse Response Compiler
License
Renewal License
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
na
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
na
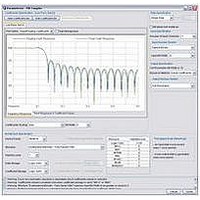
Chapter 3: Parameter Settings
Specify the Architecture Specification
Table 3–5. Fully Serial Filter Architecture
Table 3–6. Multibit Serial Filter Architecture (Part 1 of 2)
© December 2010 Altera Corporation
Data Storage
Coefficient Storage
Force Non-Symmetric
Structure
Coefficients Reload
Pipeline Level
Use Single Clock
Note to
(1) The input data bit width should be greater than or equal to four.
Number of Serial
Units
Data Storage
Coefficient Storage
Force Non-Symmetric
Structure
Parameters
Parameter
Table
3–5:
Specifies the device resources used for data storage. You can select Logic Cells, M512, M4K,
M-RAM, MLAB, M9K, M144K, or Auto. If you select Auto, the Quartus II software may store data in
logic cells or memory, depending on the resources in the selected device, the size of the data
storage, and the number of input channels.
Specifies the device resources used for coefficient storage. You can select Logic Cells, M512,
M4K, MLAB, M9K, or Auto. If you select Auto, the Quartus II software automatically selects the
most appropriate memory block size for the selected device.
The option list changes depending on which device you select. Selecting embedded memory
reduces logic cell usage and may increase the speed of the filter.
If you want to create a design that uses both symmetric and non-symmetric coefficients, turn on
this option.
Symmetric algorithms require an extra clock cycle per calculation cycle, which leads to lower
throughput.
If you want to change coefficients, turn on this option. This option is available when you choose to
store coefficients in embedded memory.
Selecting this option increases resource usage, turns off several optimization schemes, and adds
additional input ports to the filter.
Creates a higher performance filter with a resource usage increase.
Use this option when creating designs with DSP Builder. This option is only available when
Coefficients Reload is selected and M512, M4K, MLAB or M9K is specified in Coefficient Storage.
This option ties the coef_in_clk and clk signals together.
Specifies the number of serial units needed to make the filter. You can select 2, 3, or 4. The
calculation cycles of each result are reduced to one nth of the corresponding serial filter, where n is
the number of serial units. Correspondingly, there is an increase in resource utilization.
Specifies the device resources used for data storage. You can select Logic Cells, M512, M4K, M-
RAM, MLAB, M9K, M144K, or Auto. If you select Auto, the Quartus II software selects the type of
embedded memory blocks, depending on the resources in the selected device, the size of the data
storage, the number of clock cycles to compute a result, and the number of input channels.
The option list changes depending on which device you select and whether you select multirate
(interpolation or decimation). Choosing embedded memory reduces logic cell usage and may
increase the speed of the filter.
Specifies the device resources used for coefficient storage. You can select Logic Cells, M512, M4K,
MLAB, M9K, or Auto. If you select Auto, the Quartus II software automatically selects the most
appropriate memory block size for the selected device.
The option list changes depending on which device you select. Selecting embedded memory
reduces logic cell usage and may increase the speed of the filter.
If you want to create a design that uses both symmetric and non-symmetric coefficients, turn on
this option.
Symmetric algorithms require an extra clock cycle per calculation cycle, which leads to lower
throughput.
(Note 1)
(Note 1)
Description
Description
FIR Compiler User Guide
3–13