AMD-K6-2E/400AFR AMD [Advanced Micro Devices], AMD-K6-2E/400AFR Datasheet - Page 35

AMD-K6-2E/400AFR
Manufacturer Part Number
AMD-K6-2E/400AFR
Description
Manufacturer
AMD [Advanced Micro Devices]
Datasheet
1.AMD-K6-2E400AFR.pdf
(332 pages)
- Current page: 35 of 332
- Download datasheet (6Mb)
22529B/0—January 2000
2.4
Chapter 2
Centralized Scheduler
decodes. The MMX instruction decode generates a RISC86
MMX operation and, optionally, an associated MMX load or
store operation. A 3DNow! instruction decode generates a
RISC86 3DNow! operation and, optionally, an associated load or
store operation. MMX and 3DNow! instructions can be decoded
in either or both of the short decoders.
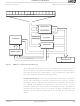
The scheduler is the heart of the AMD-K6-2E processor (see
Figure 5 on page 18). The scheduler contains the logic necessary
to manage out-of-order execution, data forwarding, register
renaming, simultaneous issue and retirement of multiple
RISC86 operations, and speculative execution.
The scheduler’s buffer can hold up to 24 RISC86 operations.
This equates to a maximum of 12 x86 instructions. When
possible, the scheduler can simultaneously issue a RISC86
operation to any available execution unit (store, load, branch,
integer, integer/multimedia, or floating-point). In total, the
scheduler can issue up to six and retire up to four RISC86
operations per clock.
The main advantage of the scheduler and its operation buffer is
the ability to examine an x86 instruction window equal to 12
x86 instructions at one time. This advantage is due to the fact
that the scheduler operates on the RISC86 operations in
parallel and allows the AMD-K6-2E processor to perform
dynamic on-the-fly instruction code scheduling for optimized
execution. Although the scheduler can issue RISC86 operations
for out-of-order execution, it always retires x86 instructions in
order.
Internal Architecture
AMD-K6™-2E Processor Data Sheet
17
Related parts for AMD-K6-2E/400AFR
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
AMD-K6 Processor
Manufacturer:
AMD [Advanced Micro Devices]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
AMD (ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES)
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
AMD CPUs, K6-2 550 MHz, Includes: Cooling Fan
Manufacturer:
AMD (ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES)

Part Number:
Description:
AMD-751ACAMD-751-TM System Controller Revision Guide
Manufacturer:
Advanced Micro Devices
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
AMD-751AMD-751-TM System Controller Revision Guide
Manufacturer:
Advanced Micro Devices
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
AMD-X5-133SFZAm5X86? Microprocessor Family
Manufacturer:
Advanced Micro Devices
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Hyper Transport PCI-X Tunnel
Manufacturer:
Advanced Micro Devices
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
HyperTransport I/O Hub
Manufacturer:
Advanced Micro Devices
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
System Controller
Manufacturer:
Advanced Micro Devices
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
AMD (ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES)
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Peripheral Bus Controller
Manufacturer:
AMD [Advanced Micro Devices]
Datasheet: