mc9s12xd256 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc, mc9s12xd256 Datasheet - Page 584
mc9s12xd256
Manufacturer Part Number
mc9s12xd256
Description
Hcs12x Microcontrollers
Manufacturer
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet
1.MC9S12XD256.pdf
(1350 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
mc9s12xd256CAA
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor
Quantity:
10 000
Company:
Part Number:
mc9s12xd256CAG
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor
Quantity:
10 000
- Current page: 584 of 1350
- Download datasheet (8Mb)
Chapter 15 Background Debug Module (S12XBDMV2)
15.4.6
BDM Serial Interface
The BDM communicates with external devices serially via the BKGD pin. During reset, this pin is a mode
select input which selects between normal and special modes of operation. After reset, this pin becomes
the dedicated serial interface pin for the BDM.
The BDM serial interface is timed using the clock selected by the CLKSW bit in the status register see
Section 15.3.2.1, “BDM Status Register
(BDMSTS)”. This clock will be referred to as the target clock in
the following explanation.
The BDM serial interface uses a clocking scheme in which the external host generates a falling edge on
the BKGD pin to indicate the start of each bit time. This falling edge is sent for every bit whether data is
transmitted or received. Data is transferred most significant bit (MSB) first at 16 target clock cycles per
bit. The interface times out if 512 clock cycles occur between falling edges from the host.
The BKGD pin is a pseudo open-drain pin and has an weak on-chip active pull-up that is enabled at all
times. It is assumed that there is an external pull-up and that drivers connected to BKGD do not typically
drive the high level. Since R-C rise time could be unacceptably long, the target system and host provide
brief driven-high (speedup) pulses to drive BKGD to a logic 1. The source of this speedup pulse is the host
for transmit cases and the target for receive cases.
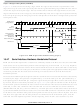
The timing for host-to-target is shown in
Figure 15-8
and that of target-to-host in
Figure 15-9
and
Figure
15-10. All four cases begin when the host drives the BKGD pin low to generate a falling edge. Since
the host and target are operating from separate clocks, it can take the target system up to one full clock
cycle to recognize this edge. The target measures delays from this perceived start of the bit time while the
host measures delays from the point it actually drove BKGD low to start the bit up to one target clock cycle
earlier. Synchronization between the host and target is established in this manner at the start of every bit
time.
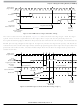
Figure 15-8
shows an external host transmitting a logic 1 and transmitting a logic 0 to the BKGD pin of a
target system. The host is asynchronous to the target, so there is up to a one clock-cycle delay from the
host-generated falling edge to where the target recognizes this edge as the beginning of the bit time. Ten
target clock cycles later, the target senses the bit level on the BKGD pin. Internal glitch detect logic
requires the pin be driven high no later that eight target clock cycles after the falling edge for a logic 1
transmission.
Since the host drives the high speedup pulses in these two cases, the rising edges look like digitally driven
signals.
MC9S12XDP512 Data Sheet, Rev. 2.17
584
Freescale Semiconductor
Related parts for mc9s12xd256
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet: