PIC18F97J60-I/PF Microchip Technology, PIC18F97J60-I/PF Datasheet - Page 109

PIC18F97J60-I/PF
Manufacturer Part Number
PIC18F97J60-I/PF
Description
IC PIC MCU FLASH 65KX16 100TQFP
Manufacturer
Microchip Technology
Series
PIC® 18Fr
Datasheets
1.PIC16F616T-ISL.pdf
(8 pages)
2.PIC18F66J65-IPT.pdf
(8 pages)
3.PIC18F66J65-IPT.pdf
(480 pages)
4.PIC18F66J65-IPT.pdf
(4 pages)
5.PIC18F66J65-IPT.pdf
(10 pages)
6.PIC18F96J60-IPT.pdf
(24 pages)
7.PIC18F97J60-IPF.pdf
(472 pages)
Specifications of PIC18F97J60-I/PF
Program Memory Type
FLASH
Program Memory Size
128KB (64K x 16)
Package / Case
100-TQFP, 100-VQFP
Core Processor
PIC
Core Size
8-Bit
Speed
41.667MHz
Connectivity
EBI/EMI, Ethernet, I²C, SPI, UART/USART
Peripherals
Brown-out Detect/Reset, POR, PWM, WDT
Number Of I /o
70
Ram Size
3808 x 8
Voltage - Supply (vcc/vdd)
2 V ~ 3.6 V
Data Converters
A/D 16x10b
Oscillator Type
Internal
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 85°C
Processor Series
PIC18F
Core
PIC
Data Bus Width
8 bit
Data Ram Size
3808 B
Interface Type
Display Driver/Ethernet/EUSART/I2C/MSSP/SPI
Maximum Clock Frequency
41.667 MHz
Number Of Programmable I/os
70
Number Of Timers
5
Operating Supply Voltage
2.35 V to 3.6 V
Maximum Operating Temperature
+ 85 C
Mounting Style
SMD/SMT
3rd Party Development Tools
52715-96, 52716-328, 52717-734, 52712-325, EWPIC18
Development Tools By Supplier
PG164130, DV164035, DV244005, DV164005, PG164120, DV164136, DM183033
Minimum Operating Temperature
- 40 C
On-chip Adc
16-ch x 10-bit
Package
100TQFP
Device Core
PIC
Family Name
PIC18
Maximum Speed
41.667 MHz
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
For Use With
AC162064 - HEADER INTFC MPLABICD2 64/80/100DM163024 - BOARD DEMO PICDEM.NET 2
Eeprom Size
-
Lead Free Status / Rohs Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
PIC18F97J60-I/PF
Manufacturer:
MICRRCHIP
Quantity:
1 800
Company:
Part Number:
PIC18F97J60-I/PF
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Quantity:
10 000
Part Number:
PIC18F97J60-I/PF
Manufacturer:
MICROCHI
Quantity:
20 000
- PIC16F616T-ISL PDF datasheet
- PIC18F66J65-IPT PDF datasheet #2
- PIC18F66J65-IPT PDF datasheet #3
- PIC18F66J65-IPT PDF datasheet #4
- PIC18F66J65-IPT PDF datasheet #5
- PIC18F96J60-IPT PDF datasheet #6
- PIC18F97J60-IPF PDF datasheet #7
- Current page: 109 of 472
- Download datasheet (8Mb)
7.2
The PIC18F97J60 family of devices can be indepen-
dently configured for different address and data widths
on the same memory bus. Both address and data
widths are set by Configuration bits in the CONFIG3L
register. As Configuration bits, this means that these
options can only be configured by programming the
device and are not controllable in software.
The BW bit selects an 8-bit or 16-bit data bus width.
Setting this bit (default) selects a data width of 16 bits.
The EMB1:EMB0 bits determine both the program
memory operating mode and the address bus width. The
available options are 20-bit, 16-bit and 12-bit, as well as
the default Microcontroller mode (external bus disabled).
Selecting a 16-bit or 12-bit width makes a corresponding
number of high-order lines available for I/O functions.
These pins are no longer affected by the setting of the
EBDIS bit. For example, selecting a 16-Bit Addressing
mode (EMB1:EMB0 = 01) disables A19:A16 and allows
the PORTH<3:0> bits to function without interruptions
from the bus. Using the smaller address widths allows
users to tailor the memory bus to the size of the external
memory space for a particular design while freeing up
pins for dedicated I/O operation.
Because the EMB bits have the effect of disabling pins for
memory bus operations, it is important to always select
an address width at least equal to the data width. If a
12-bit address width is used with a 16-bit data width, the
upper four bits of data will not be available on the bus.
All combinations of address and data widths require
multiplexing of address and data information on the
same lines. The address and data multiplexing, as well
as I/O ports made available by the use of smaller
address widths, are summarized in Table 7-2.
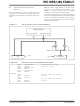
TABLE 7-2:
© 2006 Microchip Technology Inc.
Data Width
16-bit
8-bit
Address and Data Width
ADDRESS AND DATA LINES FOR DIFFERENT ADDRESS AND DATA WIDTHS
Address Width
12-bit
16-bit
20-bit
16-bit
20-bit
corresponding ports)
Multiplexed Data and
Address Lines (and
(PORTD<7:0>)
(PORTD<7:0>,
PORTE<7:0>)
Preliminary
AD15:AD0
AD7:AD0
PIC18F97J60 FAMILY
7.2.1
By default, the address presented on the external bus
is the value of the PC. In practical terms, this means
that addresses in the external memory device below
the top of on-chip memory are unavailable to the micro-
controller. To access these physical locations, the glue
logic between the microcontroller and the external
memory must somehow translate addresses.
To simplify the interface, the external bus offers an
extension of Extended Microcontroller mode that
automatically performs address shifting. This feature is
controlled by the EASHFT Configuration bit. Setting
this bit offsets addresses on the bus by the size of the
microcontroller’s on-chip program memory and sets
the bottom address at 0000h. This allows the device to
use the entire range of physical addresses of the
external memory.
7.2.2
As an extension of 20-bit address width operation, the
external memory bus can also fully address a 2-Mbyte
memory space. This is done by using the Bus Address
(BA0) bit 0 control line as the Least Significant bit of the
address. The UB and LB control signals may also be
used with certain memory devices to select the upper
and lower bytes within a 16-bit wide data word.
This addressing mode is available in both 8-Bit Data
Width and certain 16-Bit Data Width modes. Additional
details are provided in Section 7.6.3 “16-Bit Byte
Select Mode” and Section 7.7 “8-Bit Data Width
Mode”.
Address Only Lines
(and corresponding
A19:A16, AD15:AD8
(PORTE<3:0>)
(PORTE<7:0>)
(PORTH<3:0>,
(PORTH<3:0>)
PORTE<7:0>)
ADDRESS SHIFTING ON THE
EXTERNAL BUS
21-BIT ADDRESSING
AD15:AD8
AD11:AD8
A19:A16
ports)
—
Ports Available
DS39762B-page 107
PORTE<7:4>,
All of PORTH
All of PORTH
All of PORTH
for I/O
—
—
Related parts for PIC18F97J60-I/PF
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet: