PIC18F97J60-I/PF Microchip Technology, PIC18F97J60-I/PF Datasheet - Page 121

PIC18F97J60-I/PF
Manufacturer Part Number
PIC18F97J60-I/PF
Description
IC PIC MCU FLASH 65KX16 100TQFP
Manufacturer
Microchip Technology
Series
PIC® 18Fr
Datasheets
1.PIC16F616T-ISL.pdf
(8 pages)
2.PIC18F66J65-IPT.pdf
(8 pages)
3.PIC18F66J65-IPT.pdf
(480 pages)
4.PIC18F66J65-IPT.pdf
(4 pages)
5.PIC18F66J65-IPT.pdf
(10 pages)
6.PIC18F96J60-IPT.pdf
(24 pages)
7.PIC18F97J60-IPF.pdf
(472 pages)
Specifications of PIC18F97J60-I/PF
Program Memory Type
FLASH
Program Memory Size
128KB (64K x 16)
Package / Case
100-TQFP, 100-VQFP
Core Processor
PIC
Core Size
8-Bit
Speed
41.667MHz
Connectivity
EBI/EMI, Ethernet, I²C, SPI, UART/USART
Peripherals
Brown-out Detect/Reset, POR, PWM, WDT
Number Of I /o
70
Ram Size
3808 x 8
Voltage - Supply (vcc/vdd)
2 V ~ 3.6 V
Data Converters
A/D 16x10b
Oscillator Type
Internal
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 85°C
Processor Series
PIC18F
Core
PIC
Data Bus Width
8 bit
Data Ram Size
3808 B
Interface Type
Display Driver/Ethernet/EUSART/I2C/MSSP/SPI
Maximum Clock Frequency
41.667 MHz
Number Of Programmable I/os
70
Number Of Timers
5
Operating Supply Voltage
2.35 V to 3.6 V
Maximum Operating Temperature
+ 85 C
Mounting Style
SMD/SMT
3rd Party Development Tools
52715-96, 52716-328, 52717-734, 52712-325, EWPIC18
Development Tools By Supplier
PG164130, DV164035, DV244005, DV164005, PG164120, DV164136, DM183033
Minimum Operating Temperature
- 40 C
On-chip Adc
16-ch x 10-bit
Package
100TQFP
Device Core
PIC
Family Name
PIC18
Maximum Speed
41.667 MHz
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
For Use With
AC162064 - HEADER INTFC MPLABICD2 64/80/100DM163024 - BOARD DEMO PICDEM.NET 2
Eeprom Size
-
Lead Free Status / Rohs Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
PIC18F97J60-I/PF
Manufacturer:
MICRRCHIP
Quantity:
1 800
Company:
Part Number:
PIC18F97J60-I/PF
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Quantity:
10 000
Part Number:
PIC18F97J60-I/PF
Manufacturer:
MICROCHI
Quantity:
20 000
- PIC16F616T-ISL PDF datasheet
- PIC18F66J65-IPT PDF datasheet #2
- PIC18F66J65-IPT PDF datasheet #3
- PIC18F66J65-IPT PDF datasheet #4
- PIC18F66J65-IPT PDF datasheet #5
- PIC18F96J60-IPT PDF datasheet #6
- PIC18F97J60-IPF PDF datasheet #7
- Current page: 121 of 472
- Download datasheet (8Mb)
9.0
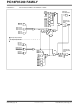
Members of the PIC18F97J60 family of devices have
multiple interrupt sources and an interrupt priority feature
that allows most interrupt sources to be assigned a high
priority level or a low priority level. The high priority
interrupt vector is at 0008h and the low priority interrupt
vector is at 0018h. High priority interrupt events will
interrupt any low priority interrupts that may be in
progress.
There are thirteen registers which are used to control
interrupt operation. These registers are:
• RCON
• INTCON
• INTCON2
• INTCON3
• PIR1, PIR2, PIR3
• PIE1, PIE2, PIE3
• IPR1, IPR2, IPR3
It is recommended that the Microchip header files
supplied with MPLAB
names
assembler/compiler to automatically take care of the
placement of these bits within the specified register.
In general, interrupt sources have three bits to control
their operation. They are:
• Flag bit to indicate that an interrupt event
• Enable bit that allows program execution to
• Priority bit to select high priority or low priority
The interrupt priority feature is enabled by setting the
IPEN bit (RCON<7>). When interrupt priority is
enabled, there are two bits which enable interrupts
globally. Setting the GIEH bit (INTCON<7>) enables all
interrupts that have the priority bit set (high priority).
Setting the GIEL bit (INTCON<6>) enables all
interrupts that have the priority bit cleared (low priority).
When the interrupt flag, enable bit and appropriate
global interrupt enable bit are set, the interrupt will
vector immediately to address 0008h or 0018h,
depending on the priority bit setting. Individual
interrupts can be disabled through their corresponding
enable bits.
© 2006 Microchip Technology Inc.
occurred
branch to the interrupt vector address when the
flag bit is set
INTERRUPTS
in
these
®
registers.
IDE be used for the symbolic bit
This
allows
Preliminary
the
PIC18F97J60 FAMILY
When the IPEN bit is cleared (default state), the
interrupt priority feature is disabled and interrupts are
compatible
Compatibility mode, the interrupt priority bits for each
source have no effect. INTCON<6> is the PEIE bit
which enables/disables all peripheral interrupt sources.
INTCON<7> is the GIE bit which enables/disables all
interrupt sources. All interrupts branch to address
0008h in Compatibility mode.
When an interrupt is responded to, the global interrupt
enable bit is cleared to disable further interrupts. If the
IPEN bit is cleared, this is the GIE bit. If interrupt priority
levels are used, this will be either the GIEH or GIEL bit.
High priority interrupt sources can interrupt a low
priority interrupt. Low priority interrupts are not
processed while high priority interrupts are in progress.
The return address is pushed onto the stack and the
PC is loaded with the interrupt vector address (0008h
or 0018h). Once in the Interrupt Service Routine, the
source(s) of the interrupt can be determined by polling
the interrupt flag bits. The interrupt flag bits must be
cleared in software before re-enabling interrupts to
avoid recursive interrupts.
The “return from interrupt” instruction, RETFIE, exits
the interrupt routine and sets the GIE bit (GIEH or GIEL
if priority levels are used) which re-enables interrupts.
For external interrupt events, such as the INTx pins or
the PORTB input change interrupt, the interrupt latency
will be three to four instruction cycles. The exact
latency is the same for one or two-cycle instructions.
Individual interrupt flag bits are set regardless of the
status of their corresponding enable bit or the GIE bit.
Note:
Do not use the MOVFF instruction to modify
any of the interrupt control registers while
any interrupt is enabled. Doing so may
cause erratic microcontroller behavior.
with
PIC
®
mid-range
DS39762B-page 119
devices.
In
Related parts for PIC18F97J60-I/PF
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet: